What is Athlete’s Foot? | What Helps Athlete’s Foot?
Chose Your Topic
What is Athlete's Foot? What Helps Athlete's Foot?
Athlete’s foot is a common health issue faced by many people and generally develops in warm, moist environments. What is athlete’s foot, and how does it spread? The feet are particularly prone to fungal infections because they sweat inside closed shoes and are exposed to external factors. Athlete’s foot causes symptoms like itching, redness, and peeling, which can negatively impact quality of life.
Fortunately, athlete’s foot is treatable, and early intervention can prevent the issue from worsening. In this article, we will answer all the questions about athlete’s foot, including how it spreads, its symptoms, and treatment methods to help you maintain healthy feet.
What is Athlete's Foot?
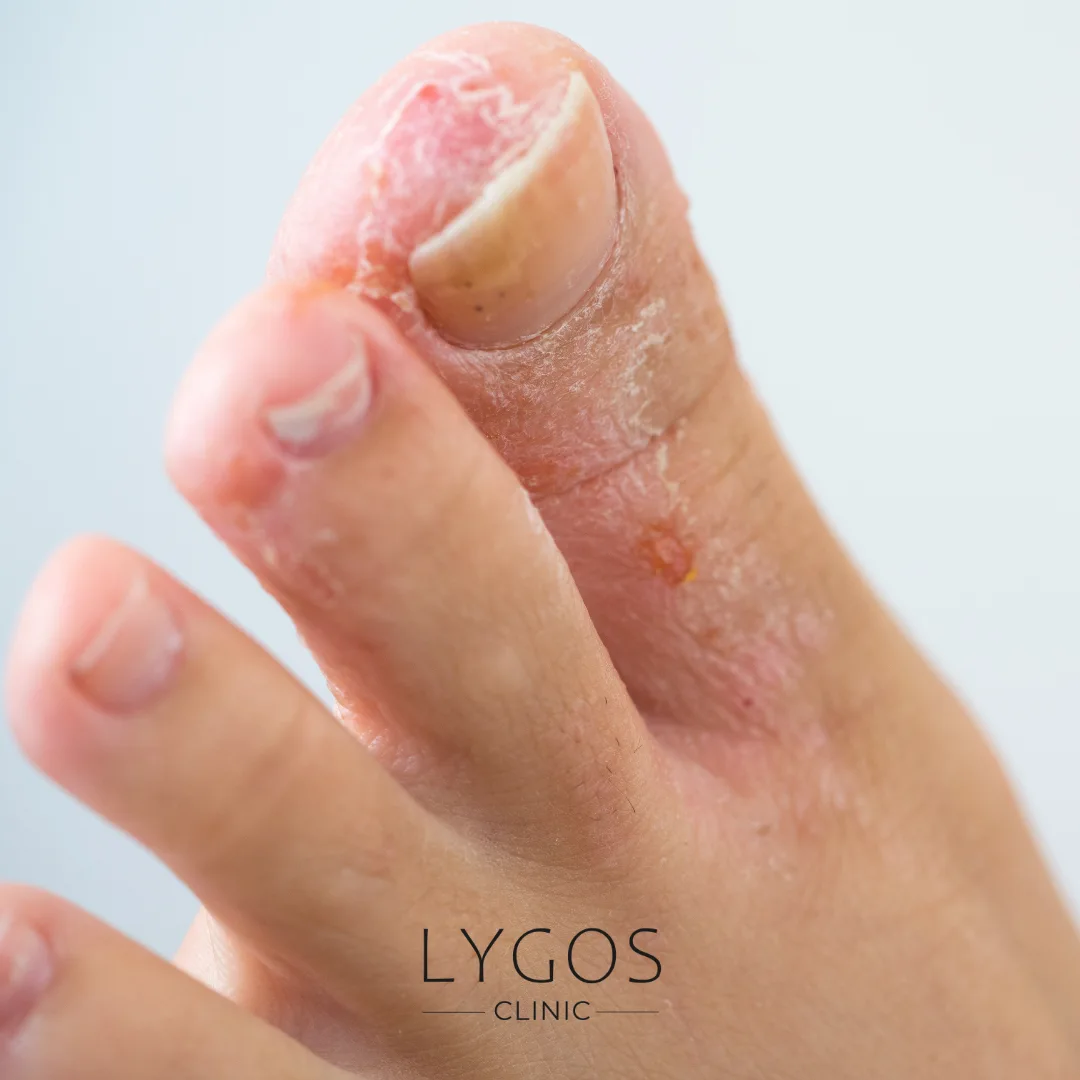
Athlete’s foot is commonly described as a microbial infection that typically appears on the toenails or between the toes. It grows on the surface of the skin, leading to itching, redness, and peeling. Warm and moist environments provide ideal conditions for fungal growth. The feet are one of the most susceptible areas of the body for such infections because sweating and frequent use of closed shoes facilitate the spread of fungi. Athlete’s foot is usually caused by a type of fungus called dermatophytes, and if left untreated, it can lead to more severe skin problems.
Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
The symptoms of athlete’s foot can vary depending on the severity and type of infection. However, the most common symptoms include:
- Itching and Burning: Itching between the toes or on the soles of the feet is the most common symptom. Some people may also experience a burning sensation.
- Redness and Swelling: Athlete's foot infection can cause redness and swelling in the affected area.
- Peeling and Flaking: As the infection progresses, the skin begins to peel and flake.
- Bad Odor: In some cases, athlete's foot infections can cause a foul smell.
- Blisters: Some types of fungi can form fluid-filled blisters on the skin.
- Pain: Mild or severe pain can be felt in the infected area.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a specialist as soon as possible. Untreated athlete’s foot can spread and deepen the infection.
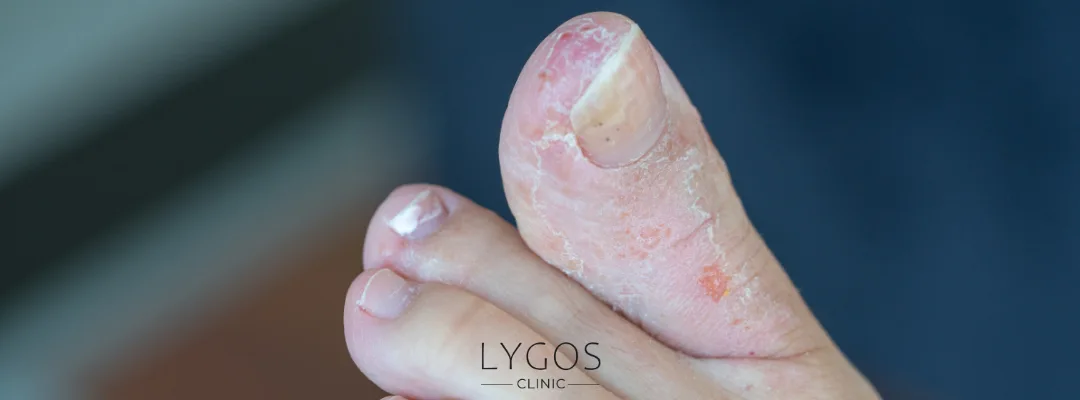
Types of Athlete's Foot
There are different types of athlete’s foot, depending on the location of the infection and the type of fungus. Here are the most common types:
- Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot): This is the most common form of athlete's foot, usually starting between the toes and sometimes spreading to the soles and heels. It often presents with itching, redness, peeling, and cracking.
- Onychomycosis (Nail Fungus): Nail fungus typically results in thickening, yellowing, and breaking of the nails. If untreated, it can lead to the complete loss of the nail.
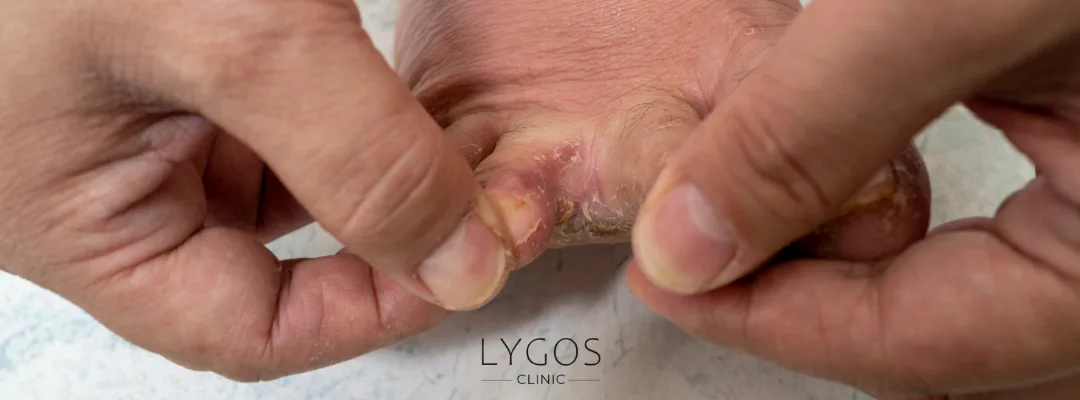
- Interdigital Tinea: This type of fungus affects the areas between the toes and often causes peeling and pain.
- Mycosis Fungoides: A more complex fungal infection that spreads deeper into the skin, leading to larger lesions. If untreated, it can leave permanent scars.
How Does Athlete's Foot Spread?
The transmission of athlete’s foot occurs mainly through direct contact. The ways in which athlete’s foot spreads include:
- Walking in Public Places: Public areas like gyms, swimming pools, saunas, and showers have a high risk of spreading fungi. Walking barefoot in these places makes it easier for fungi to spread.
- Using Other People's Belongings: Sharing personal items like shoes, socks, towels, or slippers can transmit athlete's foot.
- Tight, Airless Shoes: Wearing tight shoes causes the feet to sweat and creates a moist environment where fungi can thrive.
- Weak Immune System: People with a weakened immune system are more prone to developing athlete's foot infections.
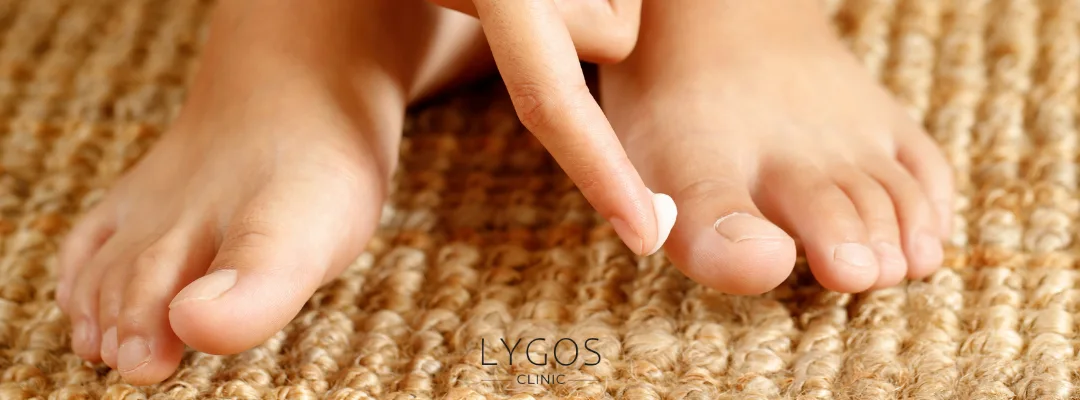

Treatment for Athlete's Foot
The treatment of athlete’s foot generally involves topical antifungal creams or sprays. In more advanced cases, oral antifungal medications may be necessary. Here are some methods for treating athlete’s foot:
- Antifungal Creams: One of the most common methods used to treat athlete's foot. These creams are applied directly to the infected area, and treatment typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
- Antifungal Sprays and Powders: These products can be used to prevent and treat athlete's foot. Antifungal sprays or powders help prevent the spread of fungi and reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
- Oral Medications: If the fungal infection is widespread and topical treatments are not sufficient, doctors may prescribe oral antifungal drugs. These medications are stronger and work throughout the body.
- Foot Care: Regular cleaning, drying, and airing of the feet are important. Tight shoes and moist environments can trigger athlete's foot, so comfortable and breathable footwear should be chosen.
What Happens if Athlete's Foot is Left Untreated?
If athlete’s foot is not treated, it can lead to the spread of the infection and serious health problems. Possible consequences of untreated athlete’s foot include:
- Spread of Infection: If untreated, athlete's foot can spread to other areas of the body, including the hands, groin, and nails.
- Deep Skin Infections: Fungi can penetrate deeper into the skin, leading to more severe infections that are harder to treat.
- Nail Loss: In cases of toenail fungus, the infection can cause the nails to become damaged, yellow, and eventually fall off.
- Secondary Bacterial Infections: Wounds and cracks caused by athlete's foot can lead to bacterial infections.
- Painful and Uncomfortable Symptoms: As the infection progresses, pain and discomfort increase, making daily activities difficult.
With proper treatment and care, athlete’s foot can be controlled. Early intervention helps prevent further spread and promotes a quicker recovery process. By taking care of your feet, you can avoid this condition and live more comfortably.
What is Athlete's Foot? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Athlete's foot is a fungal infection that commonly affects the feet, especially between the toes or on the nails. It is characterized by itching, redness, peeling, and sometimes blistering. It thrives in warm, damp environments.
Athlete's foot spreads through direct contact with infected surfaces or individuals. It is commonly contracted in public areas such as swimming pools, gyms, and shower stalls. Sharing personal items like shoes or towels can also lead to transmission.
Symptoms of Athlete's foot include itching, redness, swelling, peeling, blisters, and a foul odor. In some cases, pain may also occur in the affected area.
Athlete's foot can be treated with topical antifungal creams, powders, or sprays. In more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be required. Keeping the feet dry and clean also aids in recovery.
Athlete’s foot generally does not go away without treatment. If left untreated, the infection can spread and worsen, leading to complications such as deep skin infections or nail loss.


