HPV Warts Symptoms | Transmission and Risk Factors

Chose Your Topic
HPV Warts Symptoms
HPV warts are a common health issue today. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infections can often cause warts on the skin and in the genital area. In this article, you can find detailed information about HPV wart symptoms, types, transmission methods, treatment options, and prevention strategies.

What is HPV?
HPV, or Human Papillomavirus, is a group of viruses that can infect the skin and mucous membranes. The virus is usually transmitted through skin-to-skin contact or sexual contact. HPV belongs to a family of viruses with over 100 different types. Some HPV types cause skin warts, while others can lead to genital warts or, in more severe cases, cancer.
HPV infections often do not show symptoms, and many people may not realize they carry the virus. However, in some cases, HPV wart symptoms appear and can affect a person’s quality of life. Symptoms usually manifest as raised or flat lesions on the skin and can vary from person to person.
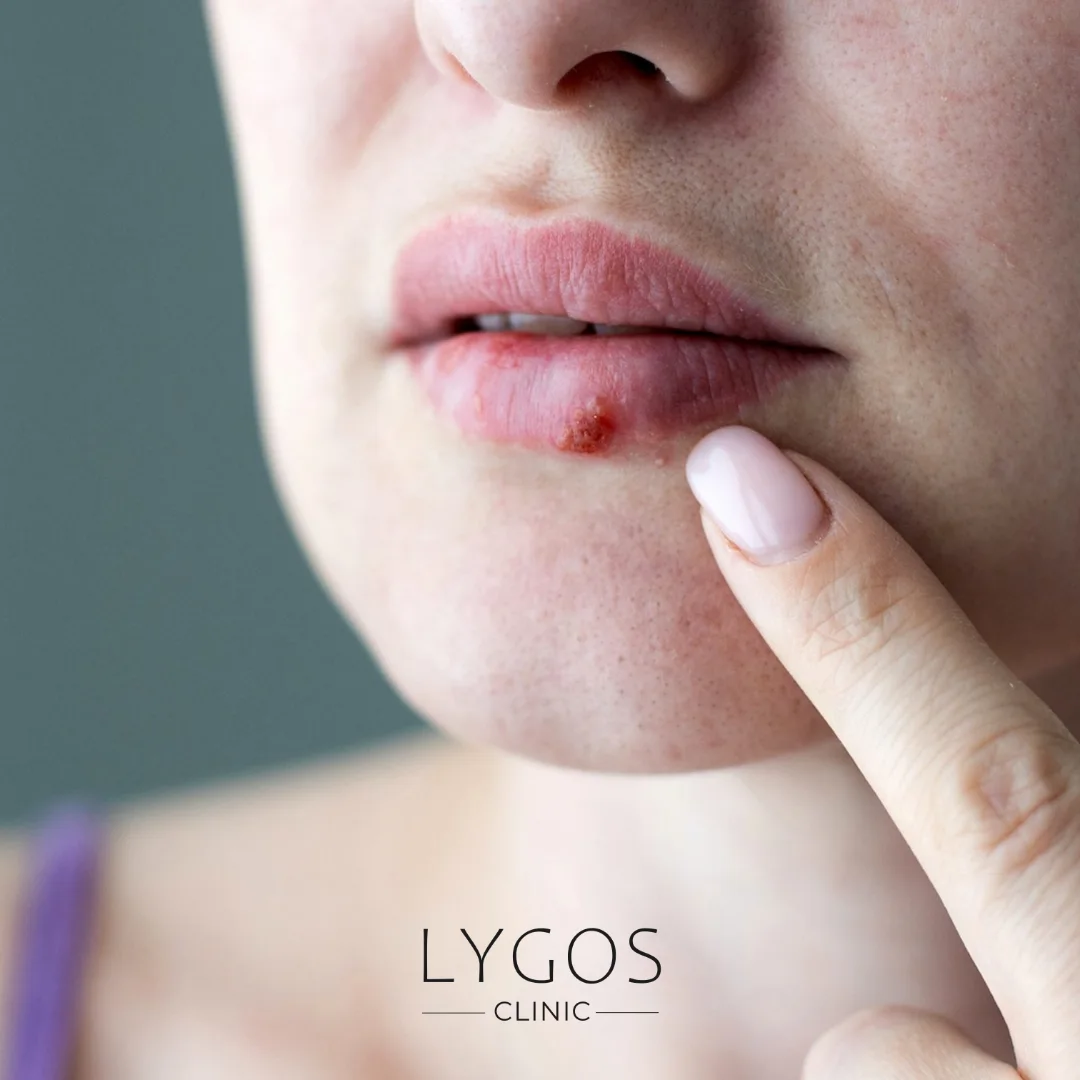
What are the Symptoms of HPV Warts?
HPV wart symptoms vary depending on the changes the virus causes in the body. HPV warts most commonly appear on the hands, feet, and genital area. Common symptoms include:
- Small, raised, or rough skin growths
- Red or flesh-colored warts in the genital area
- Itching or mild discomfort around the warts
- Painful warts on the soles of the feet due to pressure
- An increase in the number of warts over weeks or months
While HPV wart symptoms are generally harmless, they may be cosmetically bothersome. Genital warts, in particular, can affect sexual life and are contagious, so treatment is important. Some warts may disappear on their own, while others may persist for a long time.
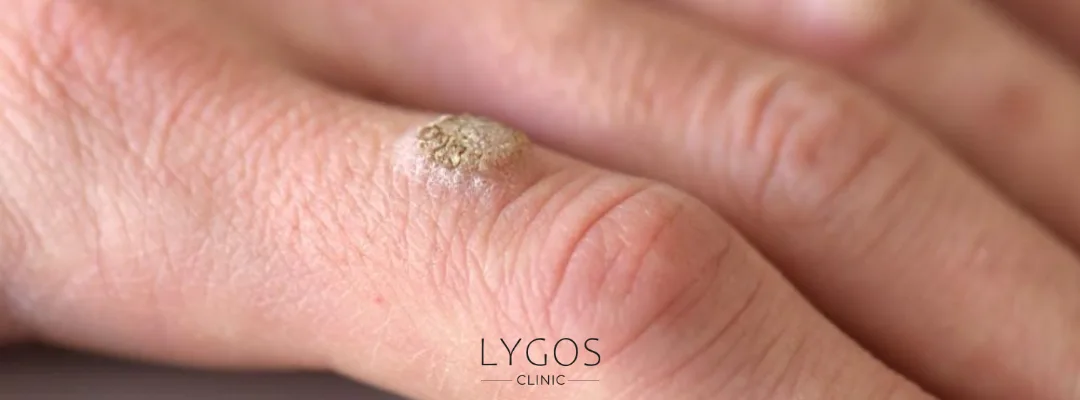
Types of HPV Warts on the Body
HPV warts appear differently depending on the virus type and the area affected. Main types of HPV warts include:
- Flat Warts: Usually found on the face and hands; flesh-colored and slightly raised.
- Hand and Foot Warts: Concentrated on hands and soles; foot warts may be painful under pressure.
- Genital Warts: Sexually transmitted HPV types cause warts in the genital area; they may appear as small clustered growths.
- Filiform Warts: Thin, long projections usually found on the neck, eyelids, or face.
- Mosaic Warts: Multiple warts merged together on the soles of the feet, forming a hard surface.
The type of wart determines the appropriate treatment method, making accurate identification important.
HPV Transmission and Risk Factors
HPV is highly contagious and can be transmitted in several ways:
- Skin contact: Direct contact with an infected person.
- Sexual contact: The most common way HPV causes genital warts.
- Shared spaces/items:Warts on the feet can spread via gyms, pools, or shared shoes.
Certain factors increase the risk of HPV infection, including a weakened immune system, multiple sexual partners, poor hygiene, and smoking. These risk factors can increase the likelihood of wart development and prolong treatment.

HPV Treatment and When to See a Doctor
When HPV wart symptoms appear, seeking proper treatment is crucial. Treatment options include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams or lotions applied directly to the wart
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the wart to remove it
- Laser Therapy: Removing resistant warts with a laser
- Surgical Removal: For large or painful warts
Doctor consultation is necessary if genital warts, rapid growth, bleeding, or pain occurs. Untreated warts may multiply, and their contagiousness continues.
HPV Vaccination and Preventive Measures
The most effective way to prevent HPV infection is vaccination. The HPV vaccine protects against most high-risk types and plays a critical role in preventing cervical cancer. Vaccination is most effective before sexual activity begins but can be given at older ages as well.
Other preventive measures include:
- Using condoms (reduces transmission risk)
- Maintaining hygiene in shared spaces
- Strengthening immunity through healthy diet and regular exercise
- Caring for hands and feet
Vaccination and these preventive strategies significantly reduce the risk of HPV wart development. Regular health check-ups are also important for early detection and treatment.
HPV wart symptoms are often visible and bothersome, but with proper treatment and prevention, they can be controlled. Awareness and early action are crucial for individual and public health. Seeking expert care when symptoms appear is the most effective way to prevent long-term complications.
HPV Warts Symptoms Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
An HPV wart is a lesion on the skin or genital area caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). These warts are usually harmless but contagious.
Warts usually appear within weeks or months after infection. In some cases, they may remain asymptomatic for a long time.
No. HPV warts can appear on hands, feet, face, and other skin areas. Genital warts, however, are transmitted sexually.
Some HPV warts may disappear over time, but others can persist and require treatment.



