How Does HPV Spread?
Chose Your Topic
How Does HPV Spread?
HPV, or Human Papillomavirus, is one of the most common sexually transmitted viruses. It can affect both women and men and often remains in the body without showing any symptoms. In this article, we will answer the question “How does HPV spread?” while also discussing the symptoms of the virus, factors that increase the risk of transmission, and ways to protect against it.
What is HPV?
HPV is a virus that causes infections in the skin and mucous membranes. There are more than 200 different types of HPV, some of which can cause genital warts, while others may lead to serious health issues such as cervical cancer. HPV infections often progress without any noticeable symptoms, and individuals may unknowingly transmit the virus to others.
Although sexual contact is the most common way HPV spreads, the virus can also be transmitted through skin contact. Therefore, understanding “How does HPV spread?” is very important.
How Does HPV Spread?
Understanding how HPV spreads is critical. The virus is most commonly transmitted in the following ways:
Sexual Contact: This is the most frequent mode of transmission. HPV can easily spread during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
Skin Contact: The virus can be transmitted through contact with areas such as the genital region, mouth, or throat.
Oral Sex: HPV can infect not only the genital area but also the mouth and throat.
During Birth: Rarely, the virus can be passed from mother to baby through the birth canal.
Many people wonder whether HPV can be transmitted without sexual contact. We will cover this in more detail in later sections. However, it should be noted that the clearest answer to “How does HPV spread?” is that it can be transmitted via skin and mucosal contact.
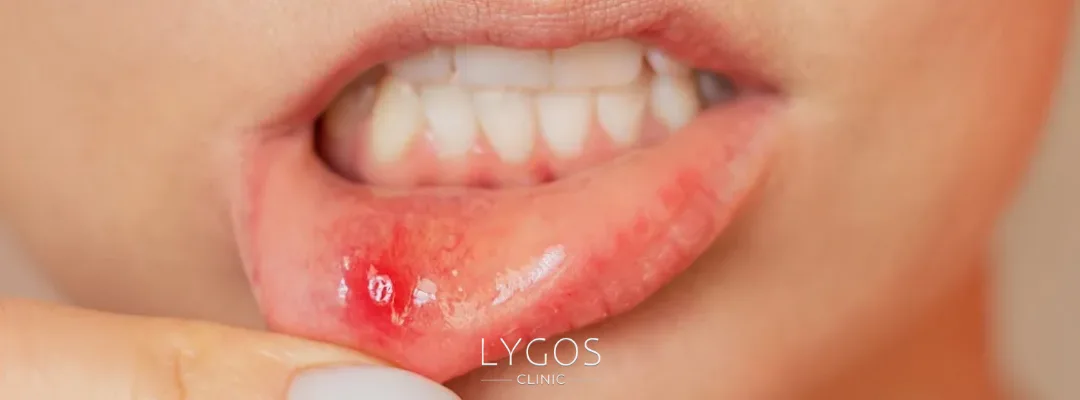
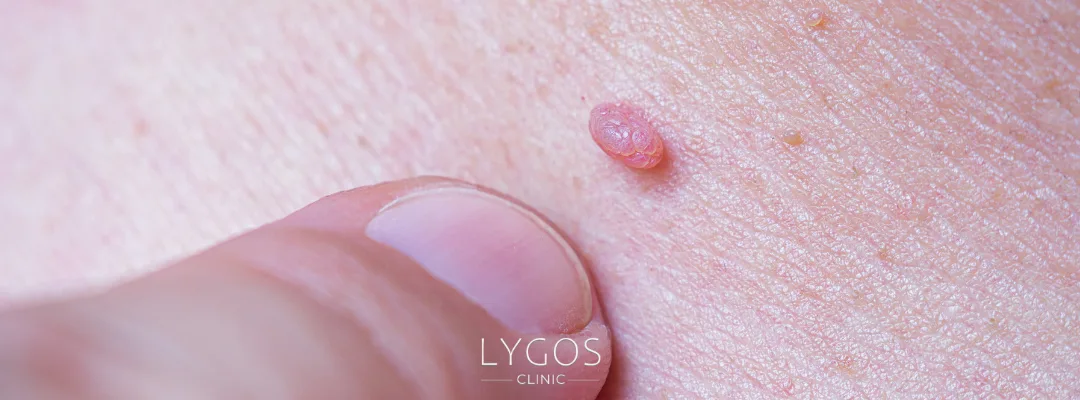
What Are the Symptoms of HPV?
HPV infections often show no symptoms. However, in some cases, the following may occur:
Genital warts
Small bumps in the vaginal or penile area
Wart-like growths in the throat or mouth
Cellular changes in the cervix during long-term infection
Because HPV infections often progress silently, individuals may not realize they are spreading the virus. Therefore, knowing “How does HPV spread?” and getting regular medical check-ups are critically important.
Factors That Increase the Risk of HPV Transmission
Several factors can increase the risk of HPV infection:
Early Sexual Activity: Starting sexual activity at a young age increases the risk of HPV.
Unprotected Sex: Not using condoms makes transmission easier.
Multiple Sexual Partners: The more partners, the higher the risk.
Immune System Problems: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infection.
Understanding these factors helps provide a clearer answer to “How does HPV spread?” Knowing the risk factors is critical for both prevention and early diagnosis.
Can HPV Spread Without Contact?
Many people wonder whether HPV can spread without sexual contact. Research shows that:
HPV mostly spreads through skin contact.
Transmission through daily activities or shared items is extremely rare.
Rarely, it can be passed from mother to baby during childbirth.
In summary, the main way HPV spreads is through sexual and skin contact. The possibility of spreading without contact is very low, and the risk in daily life is minimal.
Ways to Prevent HPV
Several effective methods exist to prevent HPV infection:
Vaccination: The HPV vaccine protects both women and men from serious types of HPV, especially when given at a young age.
Protected Sex: Using condoms reduces the risk of transmission, though it does not fully eliminate it.
Regular Check-Ups: Regular Pap smear tests are important for early detection in women.
Monogamous Relationships: Limiting the number of sexual partners reduces transmission risk.
Strengthening the Immune System: A healthy lifestyle and balanced nutrition increase resistance to the virus.
Preventing HPV is crucial for both personal health and the health of partners. Therefore, understanding “How does HPV spread?” and taking precautions is an important step in preventing the virus from spreading.
How Does HPV Spread? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Although sexual contact is the most common route, HPV can also spread through skin contact. Transmission through daily life or shared items is extremely rare.
Most people carry HPV without symptoms. When symptoms appear, they are usually genital warts, wart-like growths in the mouth or throat, and long-term cellular changes in the cervix.
Yes. Vaccination, protected sex, regular check-ups, and strengthening the immune system help prevent HPV infection.
The HPV vaccine is especially recommended for young people aged 9–26. However, it can also be given at older ages based on a doctor’s recommendation. The vaccine protects both women and men from serious types of HPV.
Most HPV infections are cleared by the body naturally. Symptoms like genital warts or cellular changes can be treated medically if they occur.



