What is Eyelid Drooping? | Symptoms and Causes

Chose Your Topic
What is Eyelid Drooping? Symptoms and Causes
Eyelid drooping, medically known as ptosis, is a condition that carries both cosmetic and functional importance. It occurs when the upper eyelid sits lower than its normal position, affecting one or both eyes. Ptosis can be present at birth or develop later in life, and while it may seem like a minor aesthetic concern, it can also narrow the visual field, interfere with daily activities, and sometimes signal more serious health problems. For this reason, the question “What is eyelid drooping?” should be addressed not only with a definition, but also with an understanding of its symptoms, causes, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.
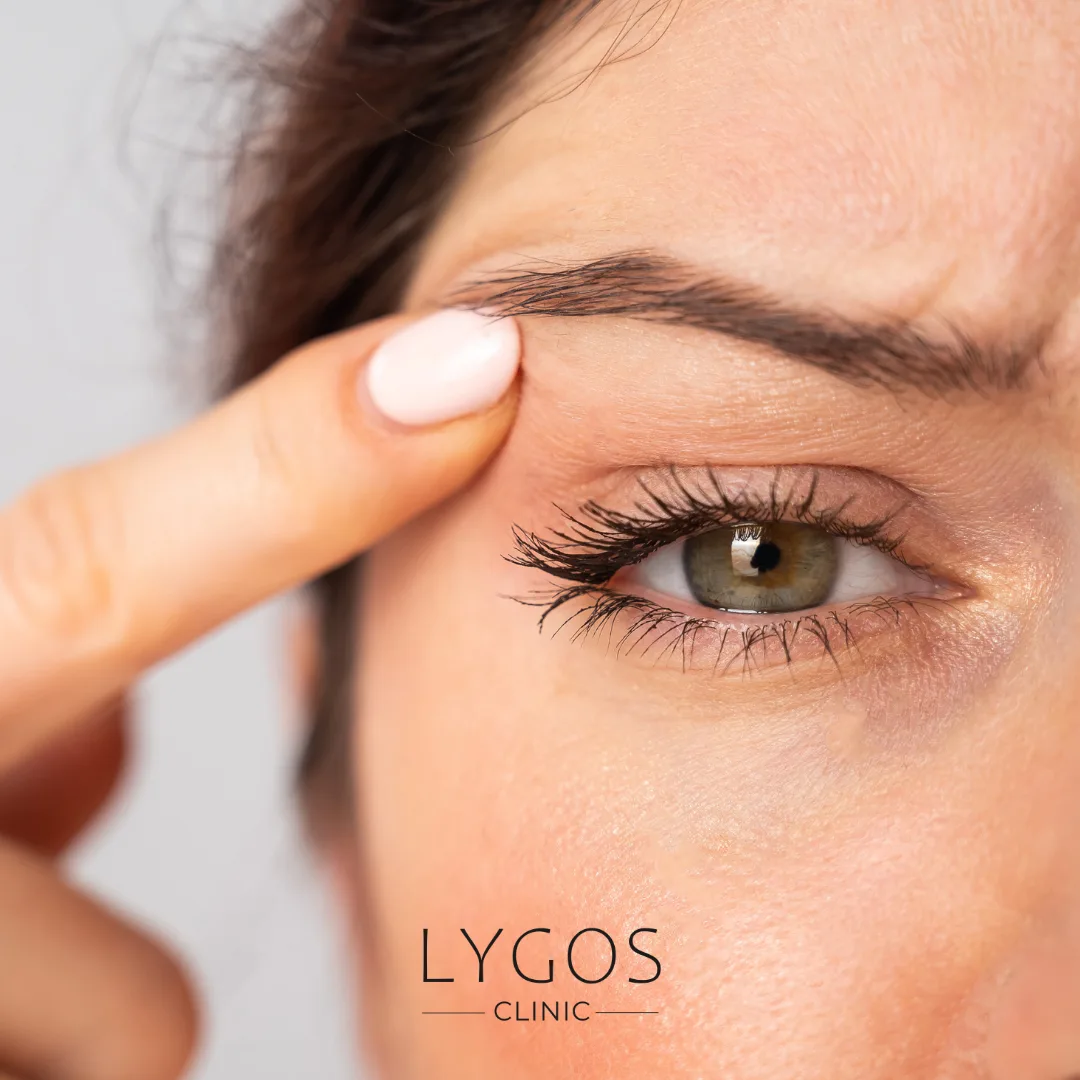
What is Eyelid Drooping?
The question “What is eyelid drooping?” is a topic frequently explored by individuals experiencing this issue. Eyelid drooping, medically known as “ptosis,” is the condition where the upper eyelid is positioned lower than normal. This problem can affect just one eye or both. Eyelid drooping can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life. Beyond cosmetic concerns, this condition can negatively impact visual quality and may sometimes be a sign of serious health problems.
What Are the Symptoms of Eyelid Drooping?
When answering the question “What is eyelid drooping?”, recognizing its symptoms is also very important. These symptoms may be both cosmetic and functional. The most commonly observed symptoms include:
- Noticeable sagging of the upper eyelid in one or both eyes
- Narrowing of the visual field
- A need to raise the eyebrows and overuse of forehead muscles
- Eye fatigue and headaches
- Asymmetrical appearance of the eyes
- Visual restrictions that may lead to learning and attention difficulties in children
These symptoms are crucial indicators that complement the answer to “What is eyelid drooping?” and early diagnosis is essential for an effective treatment process.
What Causes Eyelid Drooping?
The causes of eyelid drooping can be attributed to various congenital or acquired factors. These causes are generally categorized as follows:
- Congenital Ptosis: Occurs due to underdevelopment or weakness of the levator muscle, which lifts the eyelid.
- Age-Related (Aponeurotic) Ptosis: One of the most common causes. Arises due to the weakening or loss of elasticity of the levator muscle as one ages.
- Traumatic Ptosis: Blows to the eyelid, surgical procedures, or burns can lead to this type of drooping.
- Neurological Causes: Disorders in the brain or nervous system, such as Myasthenia Gravis, may result in eyelid drooping.
- Muscular Diseases: Conditions such as muscular dystrophy are also among the causes of eyelid drooping.
Diagnosis and Tests for Eyelid Drooping (Ptosis)
To properly answer the question “What is eyelid drooping?“, a thorough examination by an eye specialist is essential. The diagnostic process may include the following tests and evaluations:
- Examination of eyelid position and movement: The function of the levator muscle is assessed.
- Visual field analysis: Evaluates how much the drooping eyelid restricts vision.
- Photographic documentation: Used for tracking progress and comparison over time.
- Neurological assessment: Analyzes the function of the eye muscles and nerves.
- Imaging techniques such as CT or MRI, when necessary: Used to determine if there are underlying structural causes.
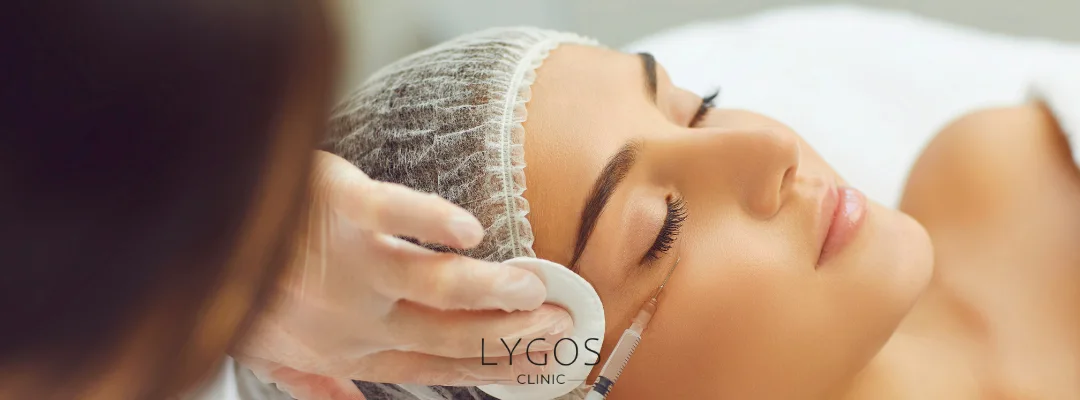

What Are the Treatment Methods for Eyelid Drooping?
When seeking answers to “What is eyelid drooping?”, understanding the treatment options is also very important. The appropriate treatment depends on the severity, cause, and the patient’s age:
- Eyelid Surgery (Ptosis Surgery): The most commonly applied treatment. It involves strengthening the levator muscle or using suspension techniques.
- Botox Applications: May provide temporary relief in milder cases but is not a permanent solution.
- Eye Exercises and Muscle Strengthening: May be effective in limited cases.
- Eyeglass Intervention: Specially designed glasses with lid-supporting devices can help expand the visual field.
Before starting treatment, it’s important to clearly understand what eyelid drooping is and what causes it.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While eyelid drooping may sometimes seem like just a cosmetic issue, certain situations require immediate medical attention. You should consult an eye specialist if any of the following occur:
- Significant narrowing of the visual field
- Sudden onset of eyelid drooping
- Presence of other symptoms like double vision or dizziness
- Risk of amblyopia (lazy eye) in children
- Inability to fully close the eyelid or eye dryness
It’s important to remember that the question “What is eyelid drooping?” is not limited to just a definition. The causes, symptoms, diagnostic process, and treatment options should be well understood and handled under medical supervision.
What is Eyelid Drooping? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Eyelid drooping can occur at any age. It may be present at birth or develop later in life due to aging. It is most commonly seen in older adults.
Depending on its cause, eyelid drooping may be either temporary or permanent. Drooping due to neurological disorders or muscle issues usually requires treatment.
If left untreated, it can restrict the visual field, cause eye fatigue, headaches, and aesthetic concerns. In children, it can lead to the risk of lazy eye.
In some mild and temporary cases, the drooping may resolve on its own. However, in most cases, medical intervention is necessary, so consulting a doctor is important.
It can be both. Beyond cosmetic concerns, eyelid drooping can affect vision and be a sign of serious health problems.



