What is Magnesium? | Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
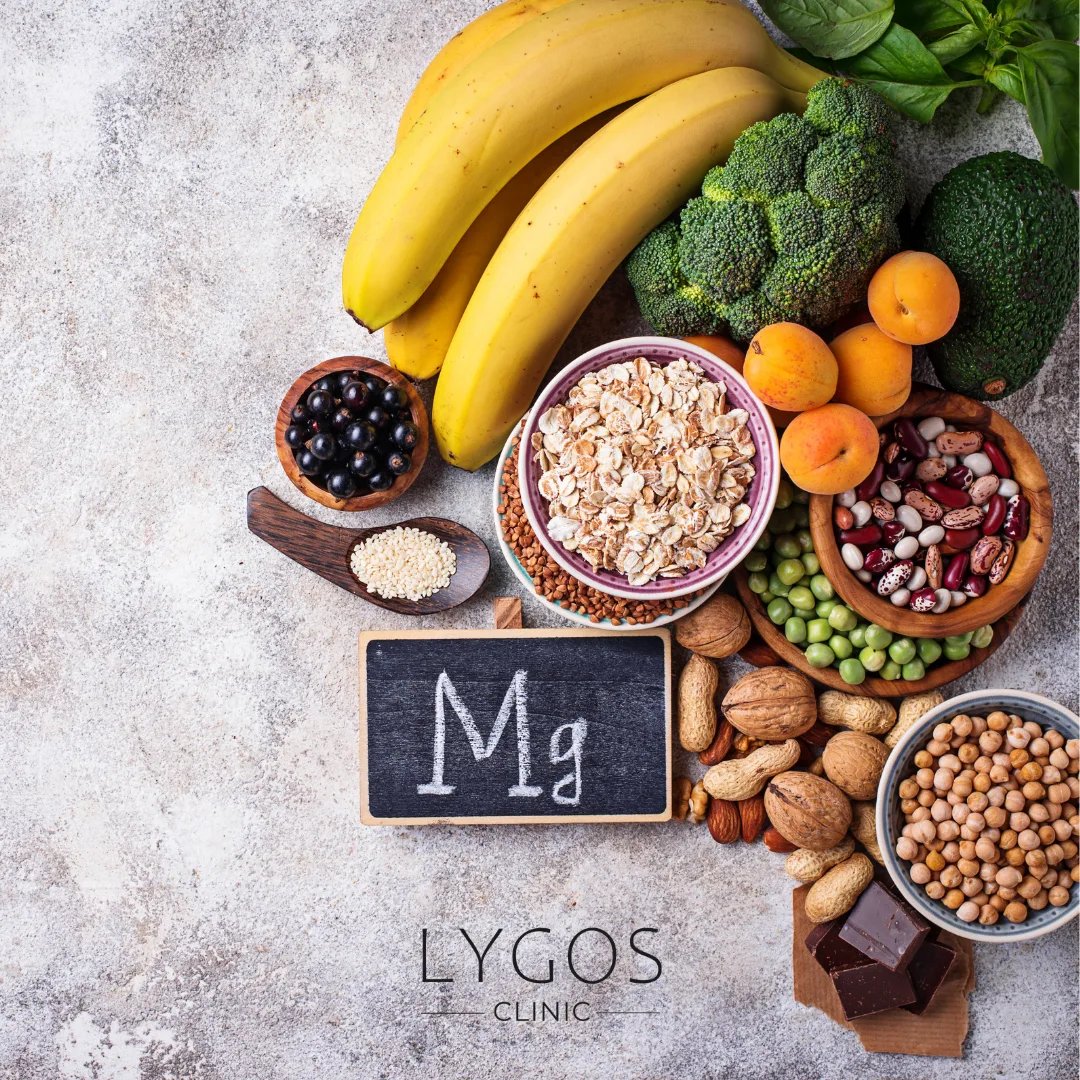
Chose Your Topic
What is Magnesium? Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium, one of the essential minerals our bodies need for a healthy life, often doesn’t get the attention it deserves. However, this valuable mineral directly affects many fundamental processes, from the nervous system to muscle functions, energy production, and bone health. So, what is magnesium and what happens in the body when it is deficient?

What is Magnesium?
The question “What is magnesium?” is frequently asked by those who want to maintain their health amid the hectic pace of modern life. Magnesium is a vital mineral involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions in the body. It plays roles in muscle functions, nerve signals, heart rhythm, immune system function, and bone development.
The human body cannot produce magnesium on its own, so it must be obtained regularly through food. It is also one of the most important minerals found abundantly in intracellular fluids.
In summary, to repeat: What is magnesium? It is a fundamental mineral that supports healthy living and carries out vital functions.
What Are the Types of Magnesium and What Are They Used For?
Magnesium comes in various forms, and each form has its own unique effects. Here are the most common types and their uses:
- Magnesium Citrate: Used to relieve constipation and treat magnesium deficiency. It has a high absorption rate.
- Magnesium Glycinate: Known for its muscle-relaxing properties. Often used for sleep disorders and anxiety.
- Magnesium Oxide: The most cost-effective form but has a low absorption rate. Commonly used to neutralize stomach acid.
- Magnesium Malate: Effective in energy production. Beneficial for those with fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Magnesium Taurate: Recommended for heart health. Supports cardiovascular function.
Choosing the most suitable form should be based on individual needs and health conditions. And let’s not forget: What is magnesium? It is not just a mineral, but also a complementary support for health.

What Are the Benefits of Magnesium?
Since magnesium supports many essential functions, it provides a wide range of benefits to the body. Here are some key benefits:
- Regulates Muscle and Nerve Functions: Balances muscle contractions and nerve signals, reduces cramps and spasms.
- Protects Bone Health: Works with calcium to increase bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
- Supports Heart Health: Helps regulate blood pressure and prevent arrhythmias.
- Supports Energy Production: Plays a role in cellular energy production.
- Psychological Well-being: May help reduce stress and alleviate symptoms of depression.
- Balances Blood Sugar: Can reduce the risk of diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity.
For all these reasons, we emphasize again: What is magnesium? It is a vital mineral with multi-faceted benefits that enhances quality of life.
Which Foods Contain Magnesium?
A balanced diet can cover most of your daily magnesium needs. Here are some magnesium-rich foods:
- Green leafy vegetables: Especially spinach, chard, and kale are rich in magnesium.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flax seeds, and pumpkin seeds are key sources.
- Whole grains: :Whole wheat, brown rice, and oats contain high amounts of magnesium.
- Legumes: Chickpeas, beans, and lentils are rich in both protein and magnesium.
- Fruits: Bananas, figs, and avocados stand out.
- Dark chocolate: Choose varieties with a high cocoa content.
Including these foods in your diet can help naturally increase your magnesium levels.
What is Magnesium Deficiency (Hypomagnesemia)?
Magnesium deficiency, also known as hypomagnesemia, occurs when blood magnesium levels are low. Since the body cannot store this mineral, regular intake is essential.
Stress, alcohol consumption, certain medications (diuretics, antibiotics), digestive system diseases, and poor nutrition can cause deficiency. It is especially common in older individuals and those with chronic illnesses.

What Are the Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency?
Magnesium deficiency can manifest through various symptoms. Some of these include:
- Muscle Pain and Cramps: Night-time muscle cramps are a common sign.
- Chronic Fatigue: A deficiency can cause fatigue due to its role in energy production.
- Mood Disorders: Symptoms of depression and anxiety may arise.
- Irregular Heartbeat: Palpitations and arrhythmias can occur.
- Insomnia: Trouble falling asleep or frequent waking.
- Digestive Issues: Loss of appetite, nausea, and mild stomach discomfort.
- Tingling and Numbness: Numbness, especially in hands and feet, may indicate deficiency.
If these symptoms are observed, it is important to consult a specialist without delay. A blood test can confirm the diagnosis and guide treatment.
In light of all this information, let’s ask again: What is magnesium? It is a mineral essential for nearly every function of the body and a cornerstone of healthy living. When not adequately obtained through diet, its deficiency can lead to serious health problems.
Therefore, incorporating magnesium-rich foods into our daily lives and using supplements under medical supervision when necessary is an important step for a healthy future.
What is Magnesium? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The recommended daily intake is approximately 310–320 mg for adult women and 400–420 mg for adult men. This requirement may vary based on age, gender, and lifestyle.
Each individual’s needs differ. Especially people with chronic conditions like kidney disease should consult a doctor before taking magnesium supplements.
Magnesium deficiency can be detected with a blood test. In some cases, special tests to measure intracellular magnesium levels may be needed.
Yes. Excessive magnesium intake can be toxic, especially for people with impaired kidney function. It may cause nausea, diarrhea, muscle weakness, and in serious cases, irregular heart rhythm.
It is generally recommended to take magnesium in the evening because of its muscle-relaxing and sleep-promoting effects. However, the timing can vary depending on individual needs.


