What is Medical Skin Care? | Eczema Treatment | LYGOS 2025

Medical Skin Care: A Comprehensive Guide to Healthier Skin
In our contemporary society, the connection between health and appearance is increasingly recognized, making medical skincare a vital aspect of overall well-being. Medical skin care offers targeted treatments aimed at helping individuals effectively manage a variety of skin concerns. This article will delve into the nuances of medical skin care, exploring its benefits, treatments, and how it differs from cosmetic skin care.
What is Medical Skin Care?
Medical skin care is a distinct area within dermatology dedicated to the assessment and management of a variety of skin disorders and ailments. Unlike general skin care, which primarily emphasizes aesthetics, medical skin care combines clinical practices with therapeutic approaches. This involves using scientifically validated products and treatments to address issues such as acne, rosacea, psoriasis, eczema, and signs of aging.
Medical skin care is often administered by licensed dermatologists and trained skincare professionals who utilize their expertise to create customized treatment plans. These plans may include prescription medications, medical-grade skincare products, and advanced procedures to promote healthier skin and improve its overall appearance.
Clinically Proven Skin Care
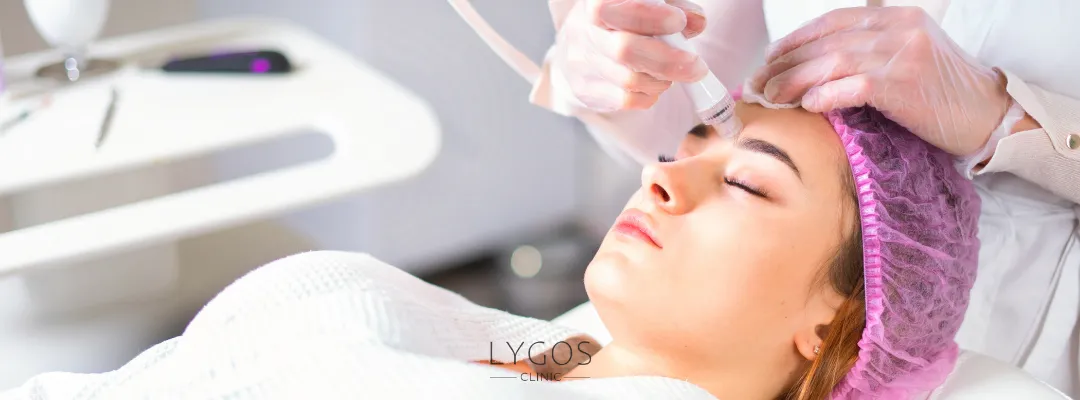

One of the hallmarks of medical skin care is the reliance on clinically proven products and treatments. Dermatologists often recommend medical-grade skincare products containing higher concentrations of active ingredients compared to over-the-counter alternatives. Certain key ingredients frequently found in clinically validated skin care products are:
- Retinoids: Known for their ability to diminish acne and visible signs of aging by enhancing cell turnover.
- Hydroquinone: Used to treat hyperpigmentation and dark spots.
- Alpha Hydroxy Acids (AHAs): These substances help exfoliate the skin, resulting in enhanced texture and tone.
- Beta Hydroxy Acids (BHAs): Effective for oily and acne-prone skin, helping to unclog pores.
- Peptides: Support skin elasticity and firmness.
When selecting skincare products, it’s important to seek advice from a dermatologist who can suggest options tailored to your skin type and individual concerns.
Medical Skin Care Treatments
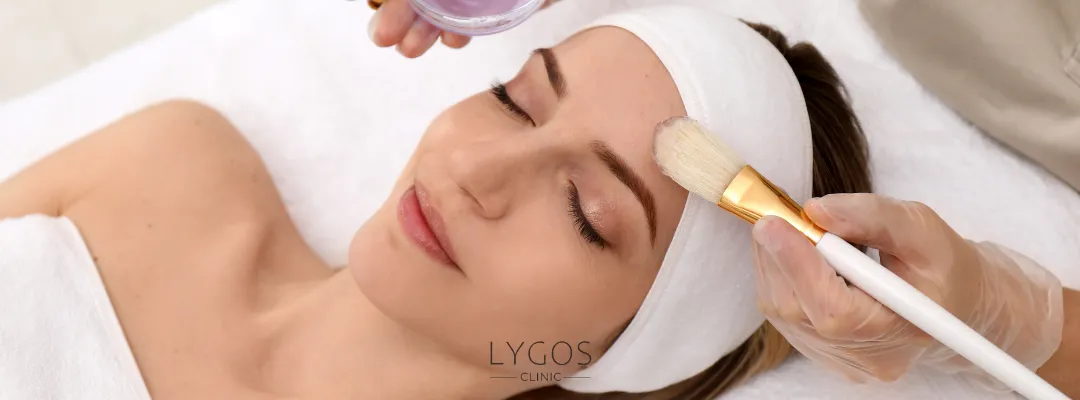

Medical skin care encompasses various treatments designed to address a range of skin issues. Here are some popular medical treatments:
Chemical Peels Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to promote the shedding of its outer layers. This process helps enhance the skin’s appearance by addressing issues like sun damage, fine lines, and uneven skin tone.
Microdermabrasion This non-invasive procedure utilizes fine crystals or a diamond-tipped wand to exfoliate the skin, effectively removing dead skin cells and stimulating the growth of new cells. Microdermabrasion is particularly useful for improving skin texture and minimizing the visibility of scars and blemishes.
Laser Therapy Laser treatments can effectively address specific skin concerns, including redness, pigmentation irregularities, and wrinkles. Various types of lasers are utilized based on the treatment goals, such as ablative lasers for resurfacing the skin or non-ablative lasers for targeting deeper skin issues.
Dermal Fillers and Botox Dermal fillers and Botox are popular medical treatments for individuals aiming to reduce wrinkles and restore facial volume. Fillers restore volume and plumpness, while Botox relaxes the muscles that cause wrinkles.
Photodynamic Therapy This treatment involves applying a photosensitizing agent to the skin, followed by light exposure to effectively treat precancerous lesions and severe acne. Each treatment is customized to match the patient’s skin type and specific condition, maximizing results while minimizing potential risks.
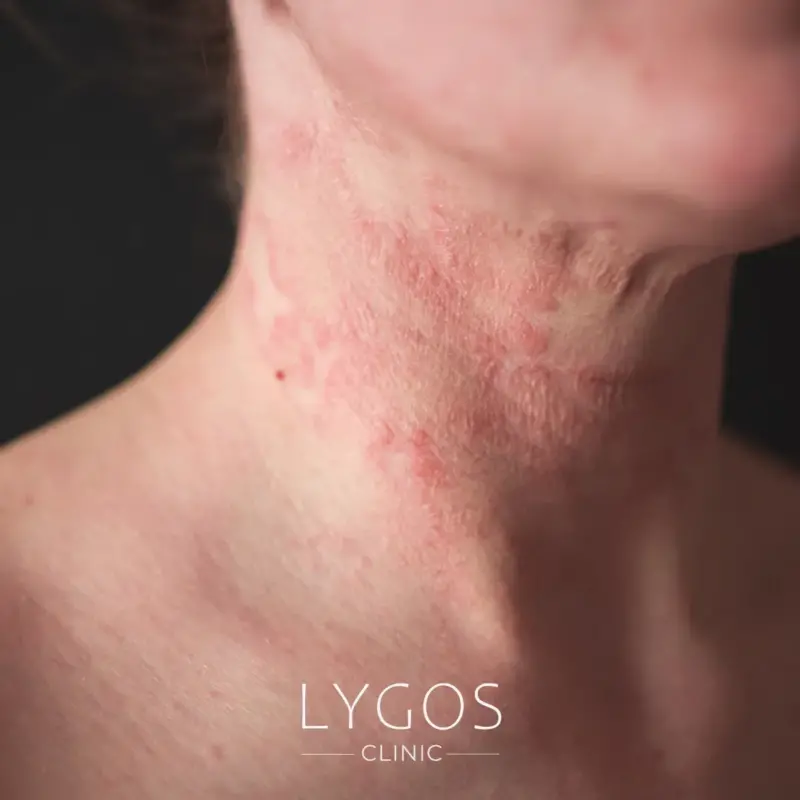
Best Eczema Treatment

Topical Treatments Prescription topical corticosteroids are often the first line of defense. They help reduce inflammation and itching. Non-steroidal topical treatments, like calcineurin inhibitors, may be recommended for use on sensitive areas of the skin.
Moisturizers Consistently applying a rich moisturizer can help retain hydration and minimize the occurrence of flare-ups. Choose products that are fragrance-free and specifically designed for sensitive skin.
Antihistamines Oral antihistamines may help alleviate itching, especially at night.
Phototherapy For individuals with moderate to severe eczema that do not improve with topical treatments, phototherapy may be a viable option. This treatment involves carefully controlled exposure to ultraviolet light, conducted under medical supervision.
Lifestyle Changes Recognizing and avoiding triggers—such as specific fabrics, soaps, or foods—can significantly aid in managing eczema symptoms. Collaborating with a dermatologist is crucial to developing a customized treatment plan that meets your skin’s specific needs.
Advanced Medical Skin Care Dermatology
Advanced medical skin care dermatology involves innovative techniques and technologies that extend beyond conventional methods. This includes advancements such as:
- Biologic Therapies: These are targeted treatments for conditions like psoriasis and eczema that operate at the level of the immune system.
- Stem Cell Treatments: Exploring the potential of stem cells for regenerative skin therapies.
- Genetic Testing: Understanding genetic predispositions to skin conditions for personalized treatment plans.
These advancements aim to improve the efficacy of treatments and provide patients with new options for managing their skin health.
What is the Difference Between Cosmetic and Medical Skin Care?
While both cosmetic and medical skin care aim to improve the appearance and health of the skin, they serve different purposes and involve different approaches:
- Cosmetic Skin Care: Primarily focuses on enhancing appearance through products and treatments designed for aesthetic purposes. This includes makeup, moisturizers, and basic skincare routines. The ingredients found in cosmetic products are frequently not subjected to clinical testing to assess their safety or effectiveness.
- Medical Skin Care: Involves diagnosing and treating specific skin conditions using scientifically backed products and treatments. Medical skin care products typically feature higher concentrations of active ingredients and are recommended by dermatologists to target specific issues like acne, hyperpigmentation, and the signs of aging.
In summary, if you’re seeking solutions for skin issues that impact your health and well-being, medical skin care is the way to go.
Facial Skin Dermatologist Near Me

Finding a qualified dermatologist for your medical skin care needs is essential. Here are a few suggestions to help you find the right facial skin dermatologist in your area:
- Referrals: Ask your primary care doctor or seek recommendations from friends and family.
- Research: Check online reviews and testimonials for local dermatologists.
- Credentials: Look for board-certified dermatologists with specialization in medical skin care.
- Consultation: Arrange a consultation to talk about your skin concerns and evaluate the dermatologist’s treatment philosophy.
- Insurance: Check to ensure that the dermatologist participates in your health insurance plan to help manage expenses.
With the right dermatologist, you can begin your path to achieving healthier, more radiant skin.
Medical skin care offers comprehensive solutions for various skin concerns, blending clinical knowledge with therapeutic treatments. From understanding the difference between cosmetic and medical approaches to exploring advanced dermatological treatments, the world of medical skin care is vast and beneficial. Whether you’re dealing with eczema, acne, or the effects of aging, seeking professional guidance from a qualified dermatologist can lead to significant improvements in your skin’s health and appearance. Prioritize your skin’s health today to reveal the possibility of a clearer, more radiant complexion.
You can click on the link to follow our social media content.