What is Oral Cancer? | Symptoms and Causes

Chose Your Topic
What is Oral Cancer? Symptoms and Causes
Oral cancer refers to malignant tumors that develop in or around the mouth (including the tongue, lips, inner cheeks, gums, palate, and floor of the mouth). It most commonly presents as squamous cell carcinoma and can spread rapidly if not diagnosed early. But what exactly is oral cancer, and why is it so important?
Oral cancer is part of the head and neck cancer group and is recognized as a serious public health issue worldwide. When detected in its early stages, the chances of successful treatment are quite high. However, many patients only seek medical attention at advanced stages because the symptoms are often overlooked.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive answer to the question, “What is oral cancer?” by exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnostic processes, and preventive measures in detail.
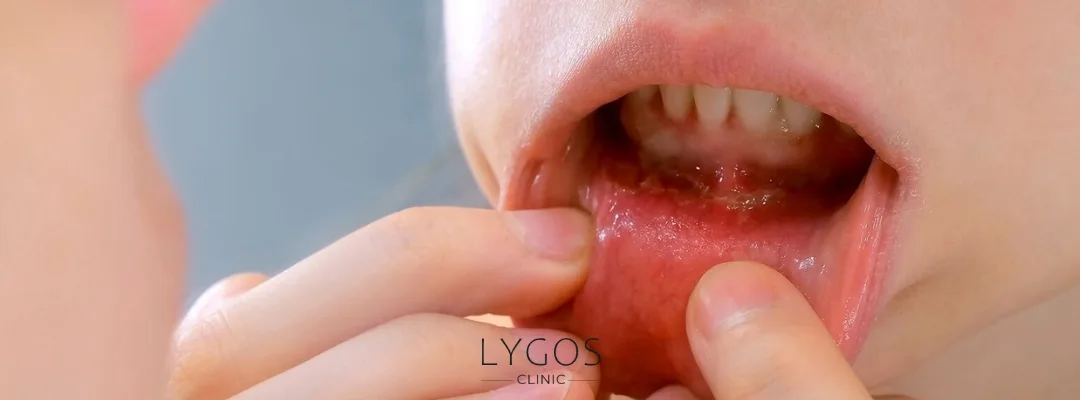
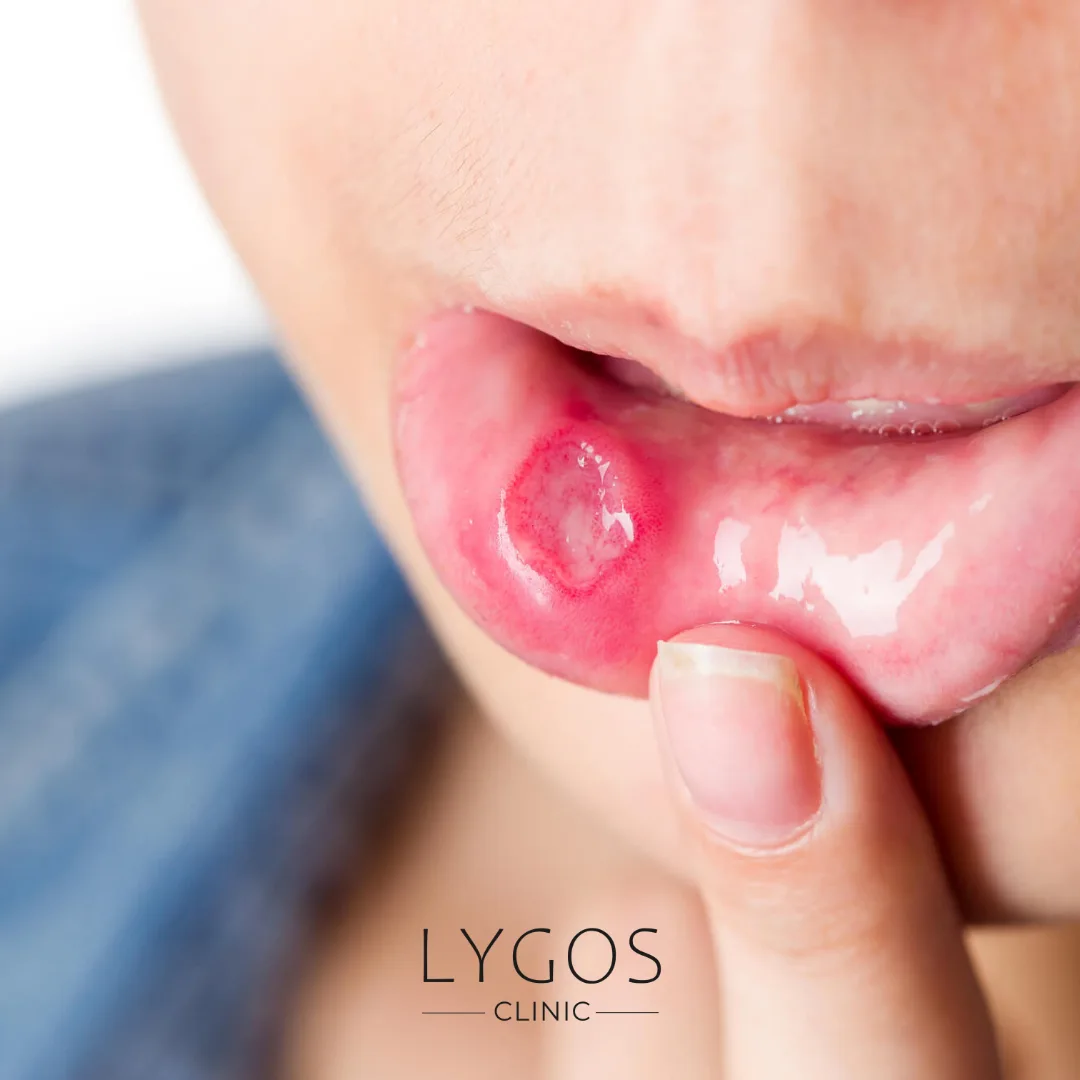
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects the tissues of the mouth and surrounding areas, including the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, and the floor or roof of the mouth. Although it is often overlooked in its early stages, oral cancer can progress rapidly and significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Recognized as part of the broader category of head and neck cancers, it remains a major public health concern worldwide. Understanding what oral cancer is, recognizing its symptoms, knowing the risk factors, and learning about diagnosis, treatment, and prevention are essential steps in reducing its impact and improving survival rates.
What Are the Symptoms of Oral Cancer?
When addressing the question “What is oral cancer?”, one of the most critical points is understanding its symptoms. Recognizing these early warning signs is vital for early diagnosis. Oral cancer commonly presents with the following symptoms:
- Persistent sores in the mouth (lasting more than 2 weeks)
- Unusual hardness or lumps in the tongue, lips, or mouth tissues
- White or red patches in the mouth (especially plaque-like)
- Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of something stuck in the throat
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in the mouth
- Hoarseness or trouble speaking
- Ear pain (particularly on one side)
- Loose teeth or dentures that no longer fit
- Lumps felt in the neck
If one or more of these symptoms are present, it is crucial to consult a specialist without delay, as each passing day reduces the chances of effective treatment.
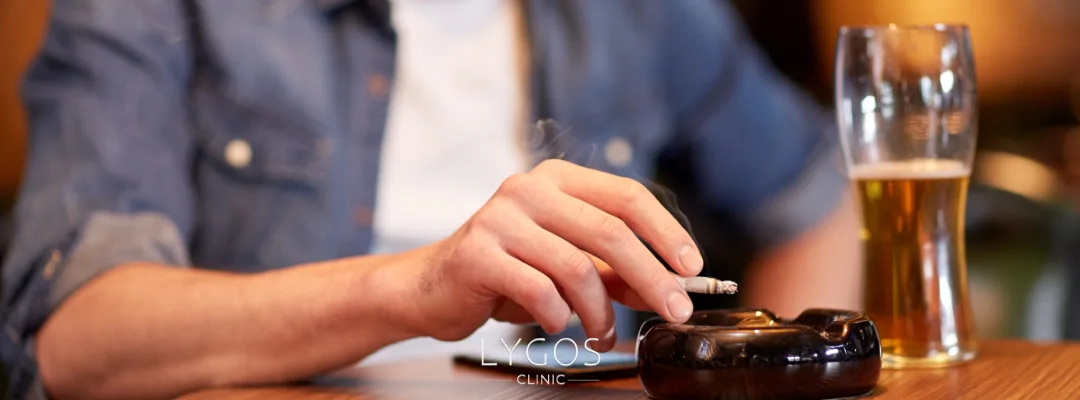

What Are the Causes of Oral Cancer?
Genetic predisposition plays a role in oral cancer development, but environmental and lifestyle factors are also significant. So, what is oral cancer, and what are the most common risk factors?
- Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Tobacco (cigarettes, pipes, cigars, hookahs, chewing tobacco) is one of the leading causes of oral cancer. Excessive alcohol consumption also damages oral tissues and increases cancer risk. The combination of tobacco and alcohol use significantly amplifies this risk.
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus): HPV, especially associated with cancers in the base of the tongue and tonsils, can considerably increase the risk of oral cancer. This virus is sexually transmitted.
- Sun Exposure: People who work outdoors are at greater risk of developing lip cancer. Long-term exposure to the sun, particularly on the lower lip, can trigger cancer formation.
- Poor Oral Hygiene and Poor Nutrition: Neglecting dental care, ignoring cavities, or having a poor diet (especially lacking vitamins A, C, and E) may create a suitable environment for oral cancer to develop.
How Is Oral Cancer Diagnosed?
When discussing “what is oral cancer,” understanding how it is diagnosed is also essential. The diagnostic process typically includes:
- Physical Examination: A thorough oral and throat examination by a dentist or ENT specialist helps identify suspicious lesions.
- Biopsy: A small tissue sample from a suspicious area is taken and sent to a lab for pathological examination. Biopsy provides a definitive diagnosis of oral cancer.
- Imaging Methods:
- CT (Computed Tomography)
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- PET Scan
These techniques help determine the extent of cancer spread and are also crucial for treatment planning.
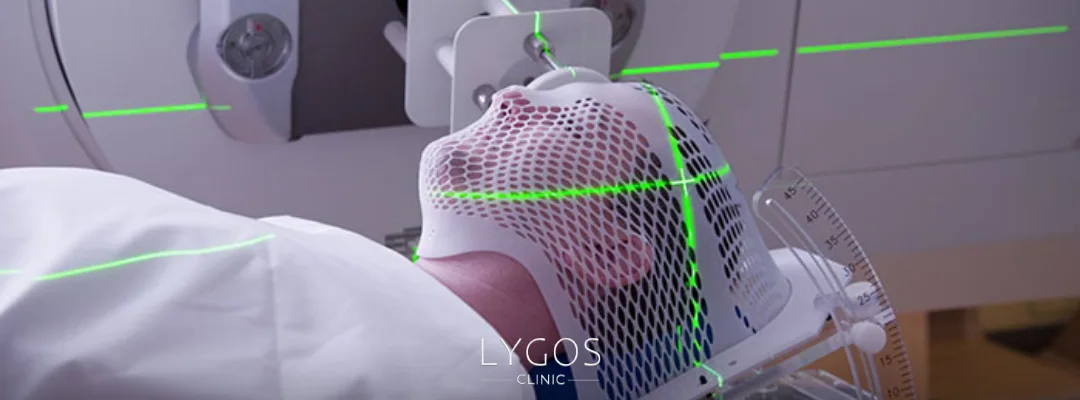
Oral Cancer Treatment Methods
After answering “what is oral cancer,” one of the most asked questions is about its treatment. The treatment of oral cancer depends on the tumor’s size, stage, and the patient’s general health. The most common treatment methods include:
- Surgical Intervention: Oral cancer diagnosed early is often successfully treated with surgery. The tumor is removed, and lymph nodes may also be cleared if necessary.
- Radiotherapy: Radiotherapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It can be used for small tumors or as an additional treatment after surgery.
- Chemotherapy: For advanced oral cancer, chemotherapy is used to prevent the spread of cancer. It is often combined with radiotherapy.
- Targeted Therapies: New-generation drugs target only cancer cells, offering treatment without damaging healthy tissues.
Ways to Prevent Oral Cancer
As important as the question “What is oral cancer?” is how to protect yourself from it. Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk:
- Quit Tobacco and Alcohol: Smoking and drinking are primary causes of oral cancer. Avoiding these habits is the most effective preventive step.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene : Regular brushing, flossing, and routine dental check-ups are essential for oral health.
- Eat a Balanced and Healthy Diet: Eating antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables protects oral tissues. A diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E strengthens the immune system.
- Get the HPV Vaccine : The HPV vaccine can reduce the risk of oral and throat cancer, especially in young individuals.
- Protect Yourself from the Sun : If you are exposed to the sun for extended periods, apply protective lip balm. Protecting yourself from harmful UV rays is important in preventing lip cancer.
As we’ve emphasized throughout this article, “What is oral cancer?” is not just a medical definition.
It is a serious health condition that directly impacts quality of life. Although early diagnosis leads to a very high treatment success rate, public awareness remains low, causing many cases to be diagnosed too late.
Remember, regular check-ups and avoiding risk factors are the most effective defense mechanisms against oral cancer. Being informed about “what is oral cancer?” can help protect both your health and the lives of your loved ones.
What is Oral Cancer? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Oral cancer involves malignant tumors in the mouth or surrounding tissues. It is more common in individuals over 40, especially those who smoke or consume alcohol. However, due to HPV infections, it is increasingly seen in younger individuals as well.
Yes, oral cancer often shows early signs such as persistent sores, patches in the mouth, and hard areas on the tongue. If these symptoms appear, see a specialist immediately. Early diagnosis greatly improves the chance of successful treatment.
No, oral cancer is not a contagious disease. However, infections like HPV, which increase the risk of oral cancer, can be transmitted.
The rate of spread depends on the type and stage of the cancer. Some types progress aggressively, while others spread more slowly. Therefore, early detection is crucial.



