Why Do Not Wisdom Teeth Erupt Properly?
Chose Your Topic
Why Do Not Wisdom Teeth Erupt Properly?
Wisdom teeth are the last molars to emerge, typically during early adulthood, and they often lead to various oral health issues. One of the most commonly asked questions about dental health is: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly? In this article, we will explore what wisdom teeth are, the signs of their eruption, why they may not come in correctly, and the problems this can cause.
What Are Wisdom Teeth?
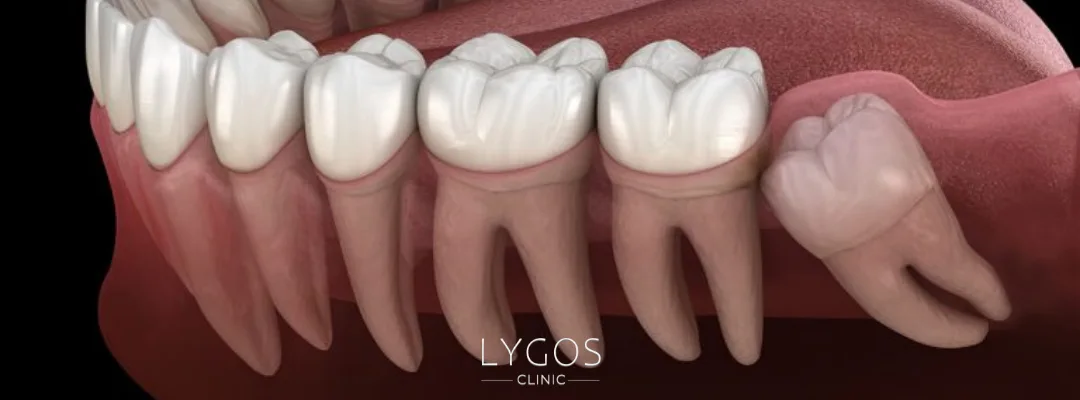
Wisdom teeth, also known as “third molars” or “twenty-year teeth,” usually emerge between the ages of 17 and 25. There are typically four of them—two on the upper jaw and two on the lower. Due to evolutionary changes, the human jaw has become smaller over time, making it more difficult for these teeth to erupt properly. As a result, many people experience impacted or misaligned wisdom teeth. This leads us to the key question: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly?
What Are the Symptoms of Wisdom Tooth Eruption?
As wisdom teeth begin to erupt, they usually present with certain signs and symptoms. Although these may vary from person to person, the most common include:
- Discomfort or pain in the jaw and gums
- Swelling, tenderness, or redness in the gums
- Difficulty opening the mouth fully
- Pain radiating to the head, ear, or throat
- Bad breath
- A sensation of pressure or crowding in surrounding teeth
When these symptoms appear, the question naturally arises: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly? The answer usually lies in the person’s jaw structure, tooth positioning, and genetics.

Why Do Not Wisdom Teeth Erupt Properly?
There are several reasons why wisdom teeth may not erupt as they should. Below, we explain the most common causes in detail:
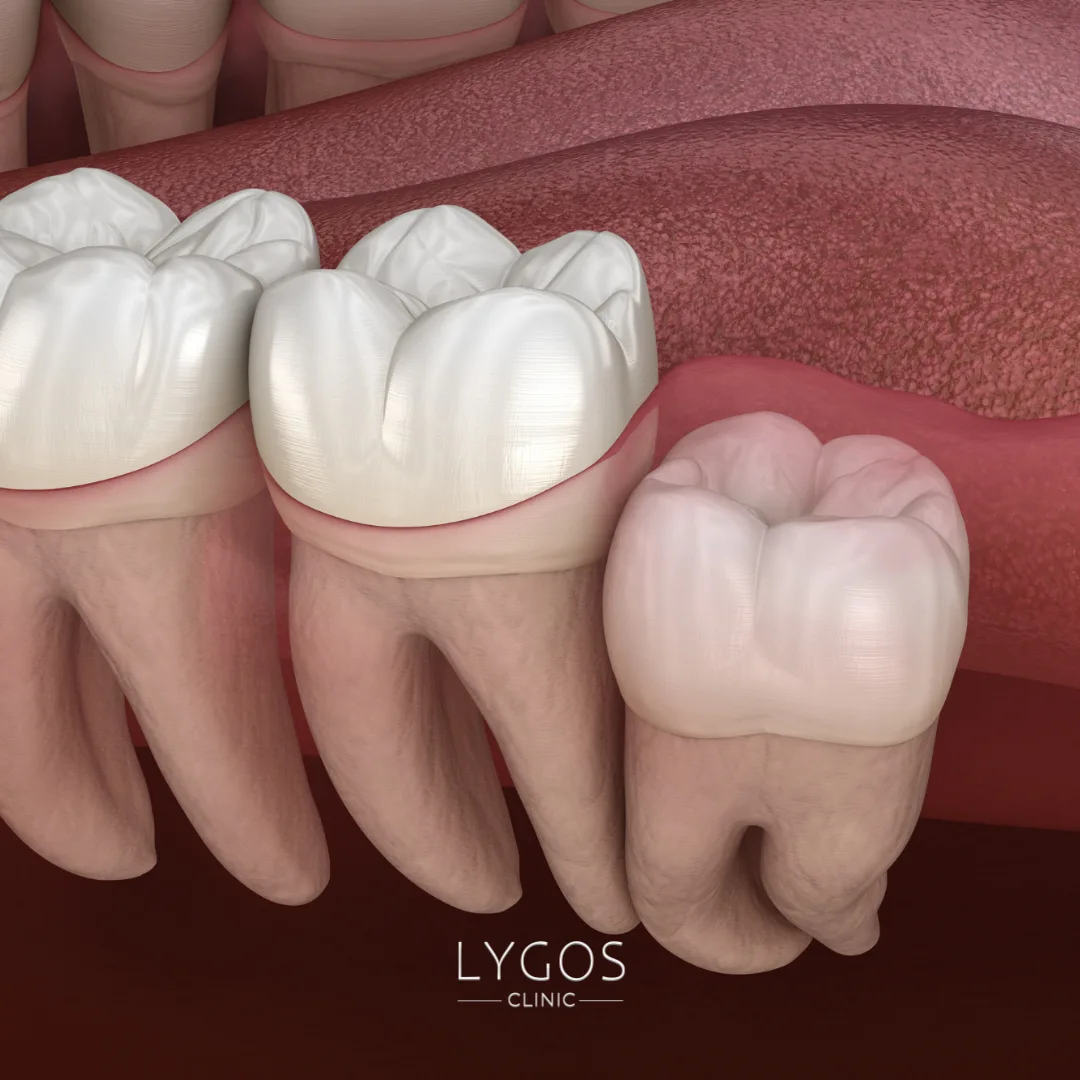
- Lack of Jaw Space: In modern humans, the jaw has gradually become smaller, which limits the space available for teeth to emerge. When there isn’t enough room, the tooth may remain impacted or emerge at an angle. This is one of the most common answers to the question: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly?
- Incorrect Tooth Position: Some wisdom teeth develop in a tilted, sideways, or even fully horizontal position. These unnatural angles can prevent eruption and may also damage nearby tissues.
- Genetic Factors : If close relatives have had problems with their wisdom teeth, you may be more likely to experience the same. Genetics can influence both jaw size and tooth orientation.
- Tooth Crowding: When the mouth is too small to accommodate all teeth, they may shift and crowd together. This often prevents the wisdom tooth from erupting properly and may leave it impacted under the gums.
All these factors contribute to answering the key question: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly?
What Problems Can Impacted Wisdom Teeth Cause?
Impacted or improperly erupted wisdom teeth can negatively affect your oral health. Some of the common complications include:
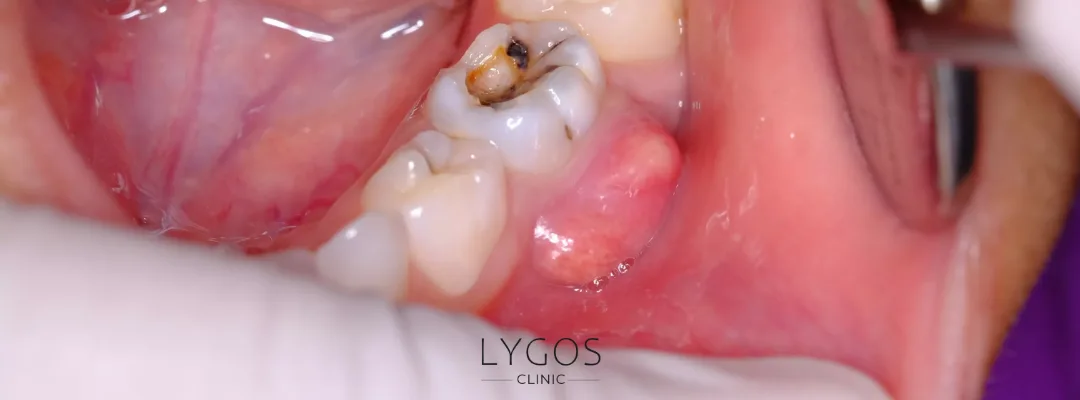
- Tooth Decay: Partially erupted or impacted wisdom teeth are difficult to clean, making them prone to bacterial buildup and decay.
- Infection and Abscess: Impacted teeth provide a breeding ground for bacteria, increasing the risk of infection and the formation of painful abscesses.
- Damage to Adjacent Teeth: Wisdom teeth that grow sideways or at an angle may press against the neighboring molars, leading to pain, decay, or root damage.
- Cyst Formation: Cysts can form around impacted wisdom teeth, which may weaken the jawbone and lead to serious structural issues.
Once again, this brings us back to the central question: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly? Addressing this early can help prevent serious oral health problems.
Why Do Wisdom Teeth Cause Pain?
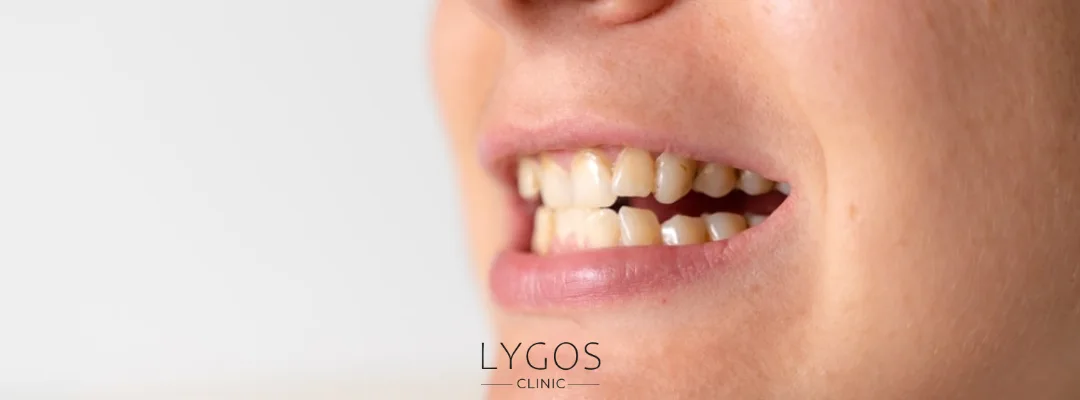
Pain is the most commonly reported symptom associated with wisdom teeth. So why does this pain occur, and how is it connected to the question, Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly?
- Gum Pressure: When there isn’t enough space, the wisdom tooth pushes against the gums to erupt, causing significant discomfort.
- Nerve Compression: Horizontally or poorly positioned wisdom teeth may press on the nerves in the jaw, resulting in widespread pain, including the jaw, ear, and head.
- Infection and Bacterial Growth: Bacterial buildup in areas that are hard to clean can lead to infections, swelling, and throbbing pain due to inflammation.
All these conditions are directly linked to improper eruption of the wisdom tooth.
Is Wisdom Tooth Extraction Always Necessary?
Not every wisdom tooth issue requires extraction, but in certain cases, removing the tooth becomes essential:
- If the tooth is fully impacted and cannot erupt
- If the tooth is coming in sideways or at an angle
- If it causes damage to adjacent teeth
- If there are recurrent infections
- If cysts or tumors form around the tooth
Your dentist will assess the situation and recommend the best course of action. Again, this emphasizes the importance of asking: Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly? Timely answers can help avoid serious consequences like tooth loss.
In conclusion, the answer to Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly? varies from person to person. Factors like jaw structure, genetics, oral hygiene, and tooth positioning all play a role. Impacted or misaligned wisdom teeth can significantly affect both oral health and quality of life.
If you’re experiencing symptoms or wondering, Why do not wisdom teeth erupt properly?, consulting with a dentist is the most effective step. Early diagnosis is essential — and dental health is no exception.
Why Do Not Wisdom Teeth Erupt Properly? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Wisdom teeth often fail to erupt properly due to insufficient jaw space, genetic factors, or abnormal tooth angles. These issues can lead to impaction or angled eruption.
Yes, mild to severe pain is common during wisdom tooth eruption. This is typically caused by pressure on the gums or infection.
A dental exam and panoramic X-ray can reveal the position and orientation of wisdom teeth to determine if they are erupting correctly.
Not always. If the tooth is not causing pain, infection, or damage to other teeth, it may not need to be extracted. However, problematic teeth often do require removal.



