What is Black Fungus | Causes and Symptoms | LYGOS 2025
Black Fungus Disease: Everything You Need to Know
Mucormycosis, commonly called black fungus disease, is a rare but potentially life-threatening infection caused by molds from the mucormycetes group. While typically uncommon, this disease has drawn global attention due to its surge among individuals recovering from COVID-19, particularly those with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes.
This illness can impact various body parts, including the sinuses, lungs, skin, and brain. Without timely treatment, it can result in serious complications or death. The symptoms of mucormycosis differ based on the area of the body affected. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of black fungus disease, including its symptoms, types, treatments, and prevention strategies.
What is Black Fungus?
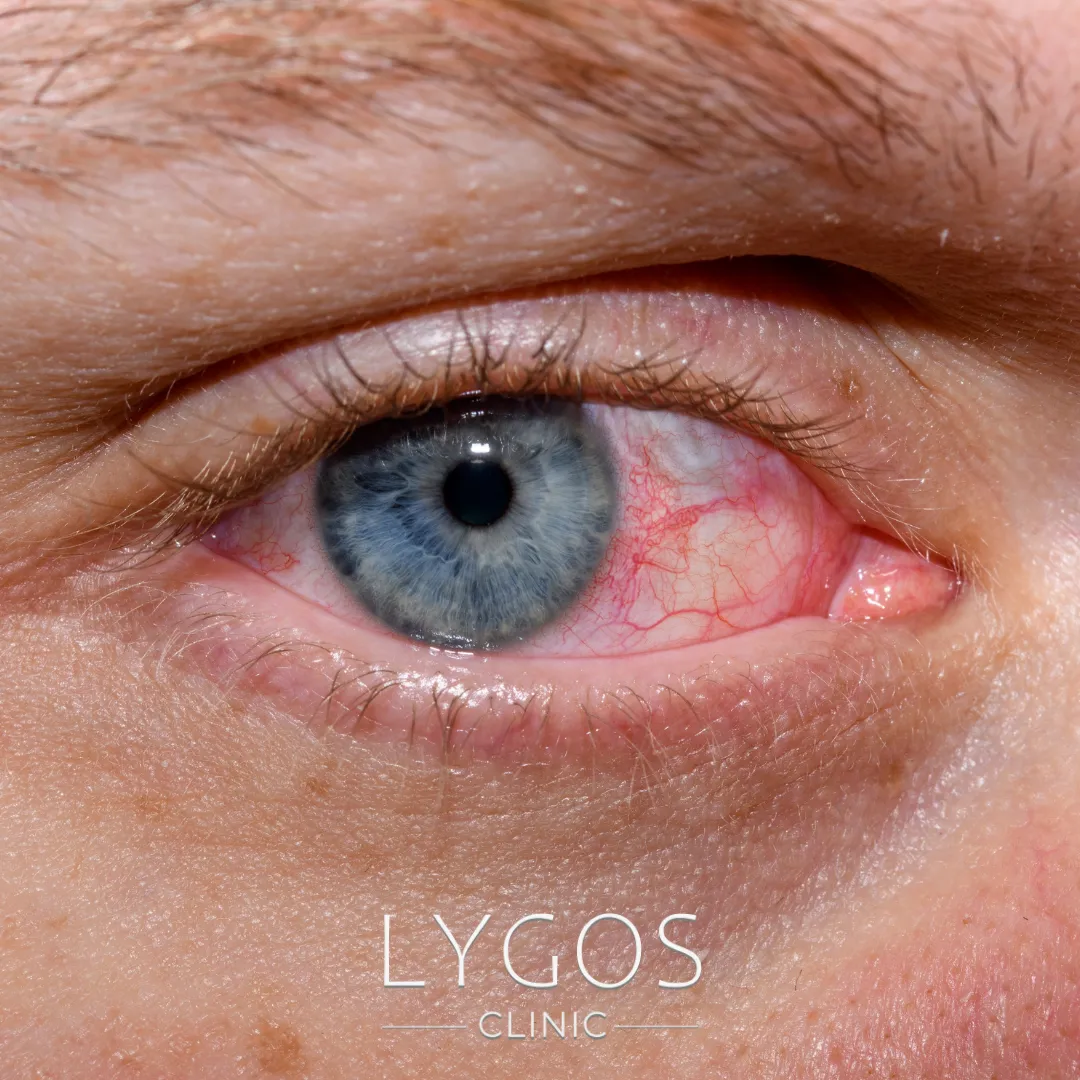
Black fungus, scientifically termed mucormycosis, is an uncommon yet serious fungal infection caused by mucormycetes molds. These molds thrive in places like soil, decayed organic material, or moist environments. While generally not harmful to healthy individuals, black fungus poses significant risks to those with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
This infection gained increased attention during the COVID-19 pandemic due to its prevalence among patients recovering from the virus, particularly in India. While it primarily affects the sinuses, lungs, skin, and brain, the infection can spread to other areas of the body under severe circumstances. Detecting and addressing the infection early is crucial, as it progresses rapidly and can become life-threatening.
What Are the Symptoms of Black Fungus (Mucormycosis)?
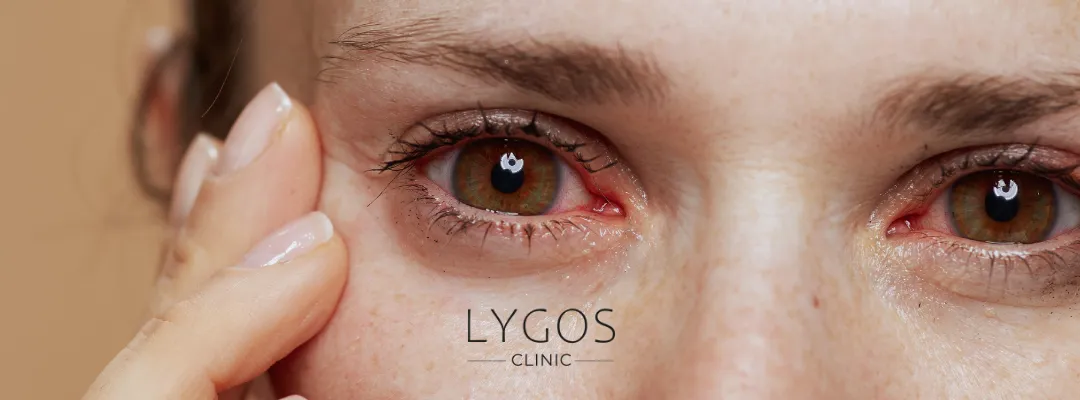
Symptoms of black fungus disease vary depending on the area of infection but may include:
1.Sinus and Nasal Symptoms:
- Nasal congestion or blockage
- Black or brown discharge from the nose
- Facial pain or swelling
2.Pulmonary (Lung) Symptoms
- Coughing (sometimes with blood)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
3.Skin Symptoms
- Blackened or discolored lesions
- Painful swelling
- Redness or warmth around the infected are
4.Neurological Symptoms (in severe cases)
- Headaches
- Vision problems
- Altered mental status
Early identification of these symptoms is critical for effective treatment. If you experience any unusual signs, consult a healthcare provider immediately.
What Are the Types of Black Fungus Disease (Mucormycosis)?
Mucormycosis can manifest in various forms, including:
- Rhinocerebral Mucormycosis: Affects the sinuses and brain, often spreading from the nasal cavity.
- Pulmonary Mucormycosis: Involves the lungs, commonly seen in patients with respiratory issues or weakened immunity.
- Cutaneous Mucormycosis: Appears as skin infections following an injury or surgery, leading to ulcers or blackened tissues.
- Gastrointestinal Mucormycosis: Primarily affects the stomach and intestines, more common in children.
- Disseminated Mucormycosis: A severe form where the infection spreads to multiple organs, including the brain.
Each type requires tailored treatment approaches to ensure the best outcomes.
Black Fungus Risk Factors
Certain conditions increase the likelihood of developing black fungus disease, such as:
- Uncontrolled Diabetes: High blood sugar weakens the immune system, allowing fungal infections to thrive.
- COVID-19 Recovery: Prolonged steroid use or oxygen therapy during COVID-19 treatment can compromise immunity.
- Weakened Immunity: Conditions like cancer, HIV/AIDS, or organ transplantation reduce the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Prolonged Hospitalization: Use of ventilators or long-term ICU stays increases exposure to fungal spores.
Managing risk factors effectively can greatly reduce the chance of contracting mucormycosis.
Treatment for Black Fungal Infection on Skin
The treatment of black fungal infections affecting the skin involves a combination of antifungal medications and surgical procedures. Antifungal drugs, such as intravenous amphotericin B, are often used to control the infection’s spread. In severe cases, surgical removal of infected or dead tissue (debridement) may be necessary to prevent the disease from advancing. Proper wound care, good hygiene, and ensuring the skin stays clean and protected are essential parts of the recovery process.
Black Fungus Causes
Black fungus is caused by mucormycetes, which enter the body through inhalation, ingestion, or skin injuries.
Key Contributing Factors
- Environmental exposure: Contact with infected soil or decaying organic materials.
- Weak immune system: Conditions like diabetes or extended use of steroids that weaken immunity.
- Hospital Environments: Exposure to unsterile medical equipment or high-humidity areas.
Raising awareness about the causes and risk factors of this disease can help in reducing the likelihood of infection.
Black Fungus Cure
While black fungus disease is treatable, it requires aggressive and timely intervention. Treatment generally combines antifungal therapy with surgical removal of affected tissues. Antifungal drugs like posaconazole or isavuconazole are commonly used alongside amphotericin B.
Surgery is often necessary to remove infected tissues, especially in advanced cases. Additionally, addressing underlying conditions like diabetes or reducing the use of immunosuppressive drugs is critical for successful recovery. Receiving early and appropriate treatment significantly improves the chances of recovery and survival.
Black Fungal Infection Symptoms
Symptoms of black fungal infection often develop rapidly and include:
- Swelling, redness, or pain in affected areas
- Tissue necrosis (blackened areas of skin)
- Fever and fatigue
- Vision impairment in severe cases
Because symptoms can mimic other conditions, proper medical evaluation is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Black Fungal Infection Treatment
The treatment for black fungal infection is multidisciplinary, requiring both medical and surgical interventions. Antifungal drugs, particularly amphotericin B, are the primary treatment option. In cases where the infection has spread, surgical removal of infected tissues is essential to stop its progression. Preventive measures, such as maintaining good hygiene, managing chronic conditions, and avoiding contaminated environments, are also crucial in preventing recurrence.
Conclusion
Black fungus disease is a serious condition requiring immediate attention and expert medical care. Understanding its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options is essential for timely intervention. By maintaining good health and managing underlying conditions, the risks of contracting mucormycosis can be minimized.


