What is Psoriasis? | Symptoms and Treatment of Psoriasis
Chose Your Topic
What is Psoriasis? Symptoms and Treatment of Psoriasis
Psoriasis, which manifests through symptoms like skin flaking, redness, and itching, is a chronic skin disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Questions like “What is psoriasis?”, “How does it develop?”, and “Is it treatable?” are among the most frequently asked about this condition.
The most accurate answer to the question “What is psoriasis?” is that it is a non-contagious disease caused by the immune system attacking skin cells, which can negatively impact quality of life. In this article, we will explore what psoriasis is and how it can be managed.
What is Psoriasis?
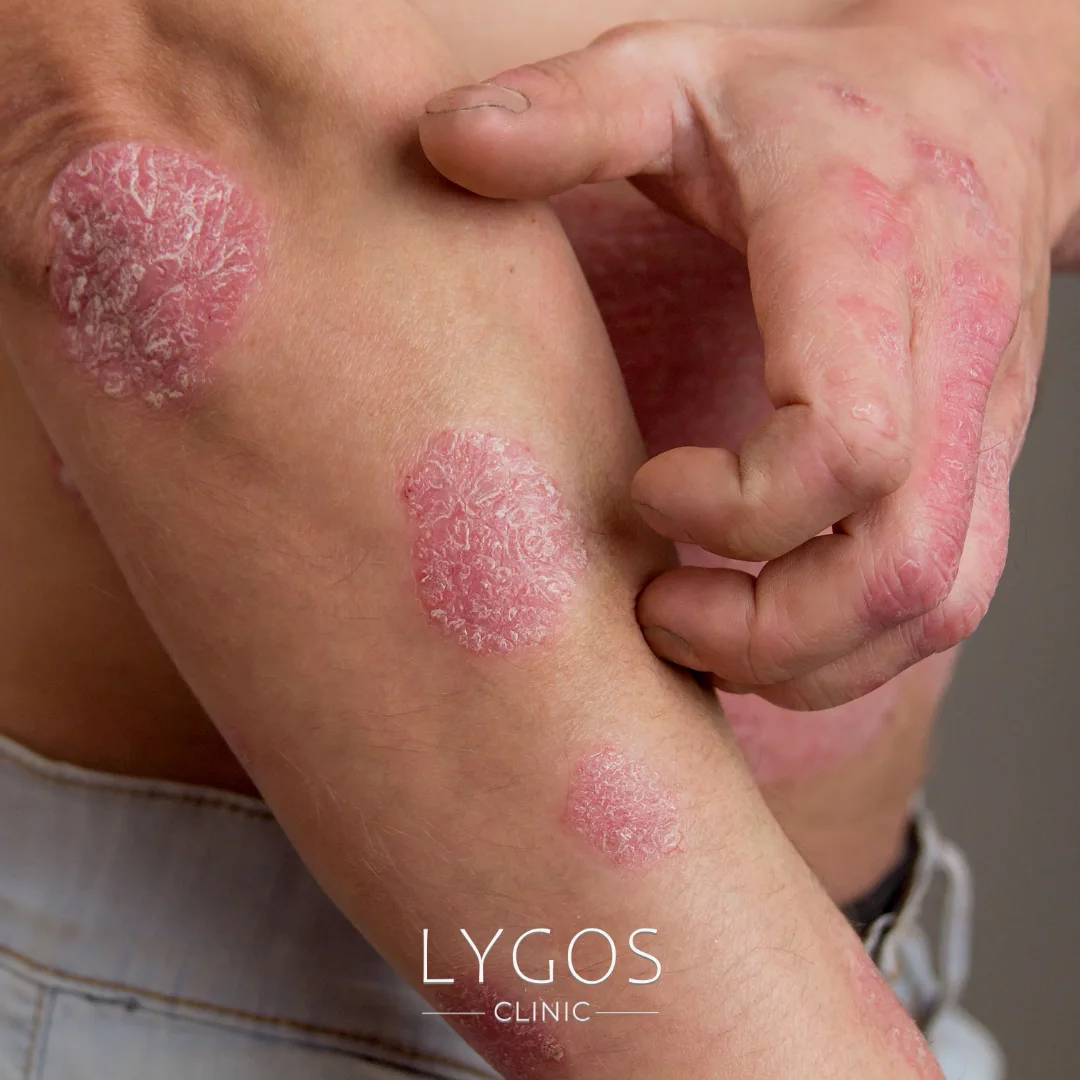
To answer the question “What is psoriasis?”, it’s important to first understand its fundamental characteristics. Medically known as psoriasis, this condition is an immune system disorder that causes skin cells to multiply much faster than normal. It leads to thick, red plaques covered with white scales on the skin.
The most important thing to know for those asking “What is psoriasis?” is that although it is not contagious, it is chronic and recurrent.
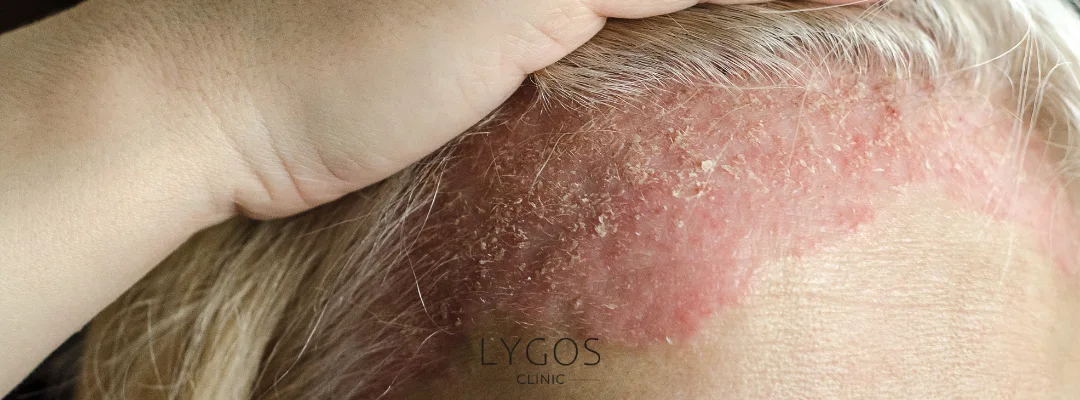
It is commonly seen on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and back, but can affect any part of the body. While many consider psoriasis to be just a skin issue, it is actually a systemic disease linked to abnormal immune responses.
Types of Psoriasis
The question “What is psoriasis?” becomes more detailed when considering its types, as this condition presents differently in each person. The most common types of psoriasis include:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most frequently seen type, characterized by thickened, scaly, and red lesions.
- Guttate Psoriasis: More common in children and young people, it appears as small drop-like lesions.
- Pustular Psoriasis: A rare but serious type marked by pus-filled blisters on the skin.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: Involves widespread redness and peeling of the skin across the entire body and can be life-threatening.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Found in body folds, it presents with shiny, red lesions.
These types illustrate the different clinical presentations that shape the answer to “What is psoriasis?”
What are the Symptoms of Psoriasis?
When asking “What is psoriasis?”, it’s essential to mention its symptoms. While symptoms may vary from person to person, the most common include:
- Redness and scaling
- Thickened patches of skin
- Severe itching and burning sensations
- Discoloration and pitting of the nails
- Cracks and bleeding in the skin
- Joint stiffness and pain
These signs offer both visual and physical clues to answer the question “What is psoriasis?”

What Causes Psoriasis?
“What is psoriasis and what causes it?” — These two questions are closely related. Psoriasis begins when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells. Although the exact cause is unknown, certain trigger factors are known:
- Genetic predisposition
- Immune system disorders
- Infections (especially throat infections)
- Stress
- Medications (e.g., lithium, beta-blockers)
- Alcohol and tobacco use
- Hormonal changes
These triggers provide both biological and environmental answers to the question, “What is psoriasis?”
What Helps with Psoriasis?
While it’s not possible to completely cure the disease, symptoms can be alleviated. Here are some helpful suggestions for those wondering “What is psoriasis?”:
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin hydrated reduces dryness and itching.
- Sunlight: Controlled sun exposure may ease lesions.
- Stress management: Techniques like meditation and yoga can reduce flare-ups.
- Healthy diet: Foods rich in omega-3 and anti-inflammatory properties are recommended.
- Warm baths: Soften the skin and relieve discomfort.
- Avoiding harsh chemicals: Be cautious with soaps and detergents.
These supportive measures offer practical answers to “What is psoriasis and how can it be managed?”
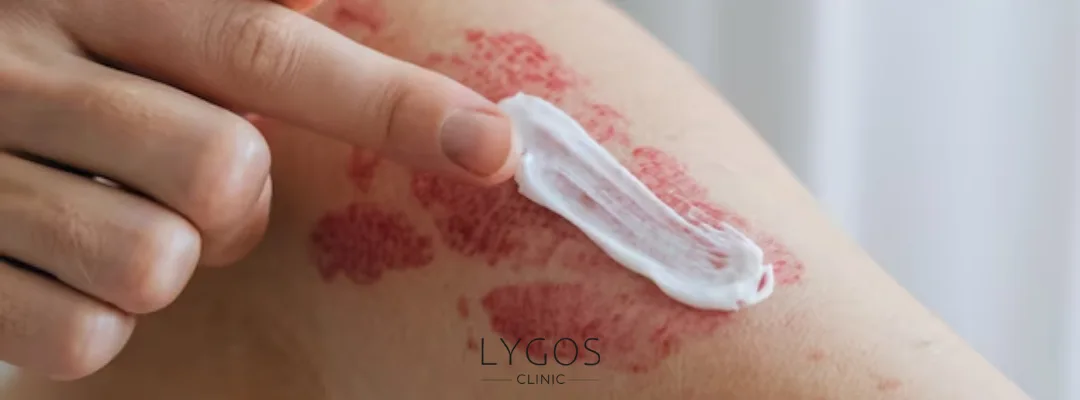
What Are the Treatment Methods for Psoriasis?
“What is psoriasis and how is it treated?” is one of the most commonly asked questions by patients. Treatments are chosen based on the severity of the condition:
- Topical Treatment : Creams and ointments are effective for mild cases. Cortisone creams and vitamin D-based products are often used.
- Phototherapy: A treatment that uses UVB light to slow down cell turnover and reduce symptoms.
- Systemic Medications: For moderate to severe cases, oral or injectable medications are used to regulate the immune system.
- Biologic Treatments: Special genetically engineered drugs that target specific areas of the immune system. Usually administered via injection and used for advanced cases.
These methods offer scientific and up-to-date answers to “What is psoriasis and what treatments are effective?”
The question “What is psoriasis?” goes beyond a simple skin disease — it refers to a systemic condition that affects a person’s quality of life. Symptoms may vary from one individual to another, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, the disease can be controlled. Managing psoriasis requires knowledge, patience, and regular medical supervision. In this article, we explored the question “What is psoriasis?” from every angle. For more information and up-to-date health content, continue following us.
What is Psoriasis? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Psoriasis is a chronic skin disease caused by abnormal immune system responses against skin cells. One of the clearest answers to “What is psoriasis?” is that it is not contagious. It does not spread through physical contact.
Unfortunately, psoriasis cannot be completely cured, but it can be well-managed with proper treatment and lifestyle changes. Periods of remission (when no symptoms are visible) are possible.
Yes, stress plays a significant role in psoriasis. High stress levels can trigger flare-ups by affecting the immune system.
Doctor-prescribed cortisone creams, vitamin D analogs, and moisturizers are commonly used. Since effects vary from patient to patient, all treatments should be used under a dermatologist’s supervision.
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory omega-3 (such as fatty fish), olive oil, green vegetables, fruits, and whole grains is recommended. Sugar, processed foods, and alcohol should be reduced.


