What is Vitamin B12? | Vitamin Deficiency | LYGOS 2025

Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a vital nutrient found naturally in foods of animal origin. It plays an important role in essential functions such as the production of red blood cells, nervous system health, cell metabolism and DNA synthesis. Deficiency of this valuable vitamin can lead to serious health problems.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to symptoms such as muscle weakness, balance and walking difficulties, sudden weight loss, nervous disorders, depressed mood, digestive problems, fatigue and heart rhythm disturbances. Therefore, regular B12 intake is essential for maintaining overall health. So, what is vitamin B12? What are the symptoms of B12 deficiency? You can find the details in our article.
What is Vitamin B12?

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a vital water-soluble vitamin that the body cannot produce on its own. It is abundant in animal foods such as dairy products, fish and meat. It has many important functions, from the production of red blood cells to the healthy functioning of the nervous system and brain.
It also plays a critical role in the synthesis of DNA, which carries the genetic code of our cells. When vitamin B12 is taken into the body, when it reaches the stomach, it is decomposed from food with the help of hydrochloric acid and enzymes, and it is released and transformed into a form ready to be used in the body. This process is very important for the vitamin to be useful.
What Does Vitamin B12 Do?

Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a vitamin that is vital for the healthy functioning of our body. This makes the question of what vitamin B12 does more curious. This vitamin is responsible for protecting blood cells and nerve cells, contributing to DNA production and supporting the health of tissues such as hair, skin and nails. It also helps prevent megaloblastic anemia, which can lead to symptoms such as fatigue and weakness.
Working together with folic acid, B12 plays a critical role in the production of the myelin sheath that covers and protects nerve cells. It also strengthens the immune system and contributes to protein metabolism.B12 deficiency can cause serious health problems. Anemia is the most common consequence of this deficiency and can make a person feel sluggish and tired all the time. Symptoms such as pale skin and shortness of breath can be observed. At more advanced levels, neurological symptoms such as forgetfulness, difficulty speaking, tingling in the hands and feet can occur. Loss of appetite, weight loss and digestive problems are also possible effects of B12 deficiency.
What are the Benefits of Vitamin B12?

Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient that protects nerve cells, prevents nerve damage and contributes to fertility. It helps cells to regenerate, grow healthy and long-lasting. It is also a vitamin that supports the healthy development of nerve endings. Adequate intake of vitamin B12 can also help to strengthen memory and increase learning ability.
The benefits of vitamin B12 can be summarized as follows:
- It supports the fast and correct functioning of the nervous system, so that neural functions become more efficient.
- Adequate B12 intake can reduce the risk of dementia, as B12 deficiency is associated with poor cognitive function.
- B12 prevents fatigue by energizing the body thanks to the organic compounds it contains.
- It works together with folic acid to provide effective protection against anemia.
- It regulates sugar metabolism by converting carbohydrates into energy and ensures more efficient use of body sugar.
- It protects cardiovascular health by lowering homocysteine levels in the blood, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
Therefore, vitamin B12 has a very important role in maintaining our health and a balanced intake is of great benefit.
What is B12 Deficiency?
B12 deficiency is a serious health problem that occurs as a result of malnutrition, the use of certain medications or metabolic problems that interfere with the absorption of the vitamin. This deficiency disrupts the proper functioning of the body, leading to various symptoms. Common symptoms of B12 deficiency include anemia, constant fatigue, memory problems, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, loss of appetite and weight loss. In addition, mouth sores, shortness of breath and pale skin color are also signs of deficiency. Therefore, it is vital to get the B12 the body needs.
What are B12 Deficiency Symptoms?

Vitamin B12 deficiency causes the body to be unable to produce enough red blood cells, which severely reduces oxygen-carrying capacity. The most obvious sign of this condition is anemia. With anemia, symptoms such as shortness of breath, heart palpitations, muscle weakness, constant fatigue, tingling in the hands and feet appear. Pale skin and weight loss are also common symptoms of B12 deficiency. So, what are B12 deficiency symptoms?
- Anemia
- Persistent fatigue and low energy levels
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Numbness or tingling in the hands, arms and legs
- Memory problems, forgetfulness
- Pale skin and feeling cold
- Mood changes such as depression, irritability and anxiety
- Difficulty focusing and concentrating
- Hair loss
- Muscle weakness
- Digestive problems: diarrhea, constipation, nausea
- Mouth sores
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Vision problems
- Mental retardation in infants and children
If a person experiences prolonged forgetfulness, poor concentration or memory loss, it is strongly recommended to consult a doctor for B12 deficiency.
What Contains Vitamin B12?
Vitamin B12 cannot be produced naturally by the body, so it must be obtained from animal foods. The richest sources of this vital vitamin include red meat, offal, poultry, fish and shellfish, eggs and dairy products. While vitamin B12 is found in high amounts in animal foods, for vegans and vegetarians, the intake of this vitamin requires more attention.
What contains vitamin B12? The following answers can be given to the question:
- Protein-rich foods such as red meat and chicken
- Seafood such as oysters, tuna, shrimp, trout, salmon and sardines
- Offal such as liver, kidney and spleen
- Milk and dairy products such as yogurt, cheese
- Vegetables such as spinach, beets, zucchini, mushrooms and potatoes (may contribute indirectly)
- Beans, peas and lentils from legumes
Vitamin B12 is concentrated in milk and dairy products, but can also be obtained from some plant sources such as fermented soy products. However, omega-3-rich nuts and fruit and vegetable groups do not contain vitamin B12. It is therefore important to maintain a balanced diet with these foods.
How is Vitamin B12 Deficiency Treated?
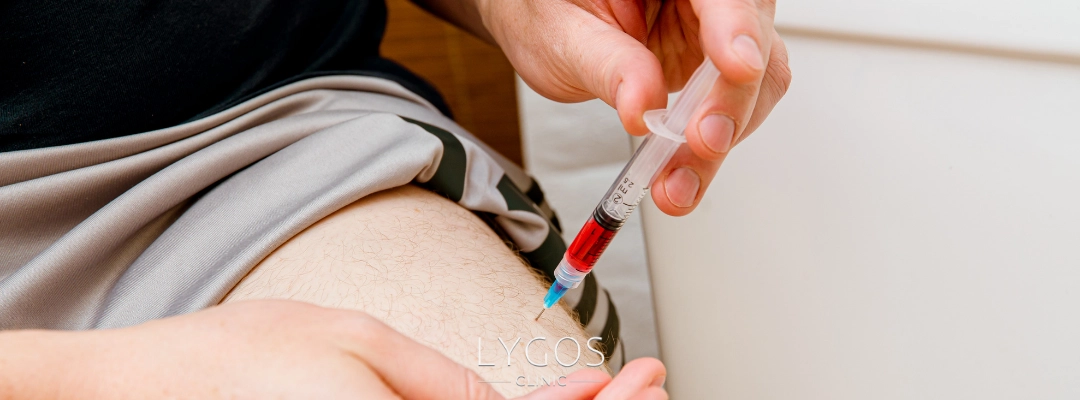
Vitamin B12 deficiency is usually treated with high-dose B12 supplements or B12 injections. While oral treatment is generally preferred in children, B12 injections are used as a more effective method in people with inadequate B12 absorption due to stomach and intestinal problems. This treatment process significantly improves people’s quality of life by eliminating the deficiency. However, if B12 deficiency is left untreated, irreversible neurological damage can occur.
B12 deficiency is also seen as a serious problem in infants and should be treated as soon as possible. A daily B12 supplement of 6-30 micrograms is recommended, especially for those with intestinal problems, people over 50, vegetarians and women planning to become pregnant. It is also important to determine the cause of the deficiency; if there is a dietary B12 deficiency (especially common in vegetarians), B12 pills or sublingual tablets may be effective.
For B12 to be properly absorbed in the body, the pancreas, stomach and small intestines must function normally. People who experience absorption problems should consult a doctor immediately. B12 deficiency should not be neglected in order to avoid more serious health problems in the later stages, and a specialist should be consulted for the most appropriate treatment dose according to the blood level.


